Many Medical Mnemonics for Memorization

This is a list of medical mnemonics. They are meant to help people study and memorize important information. Note that I did not personally create any of these. If you know of any useful ones that are not mentioned here, list them in the comments at the bottom of this page.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
A
Abdominal Pain, acute, differential diagnosis: ABDOMINAL
Appendicitis
Biliary tract disease
Diverticulitis
Ovarian disease
Malignancy
Intestinal obstruction
Nephritic disorders
Acute pancreatitis
Liquor (ethanol)
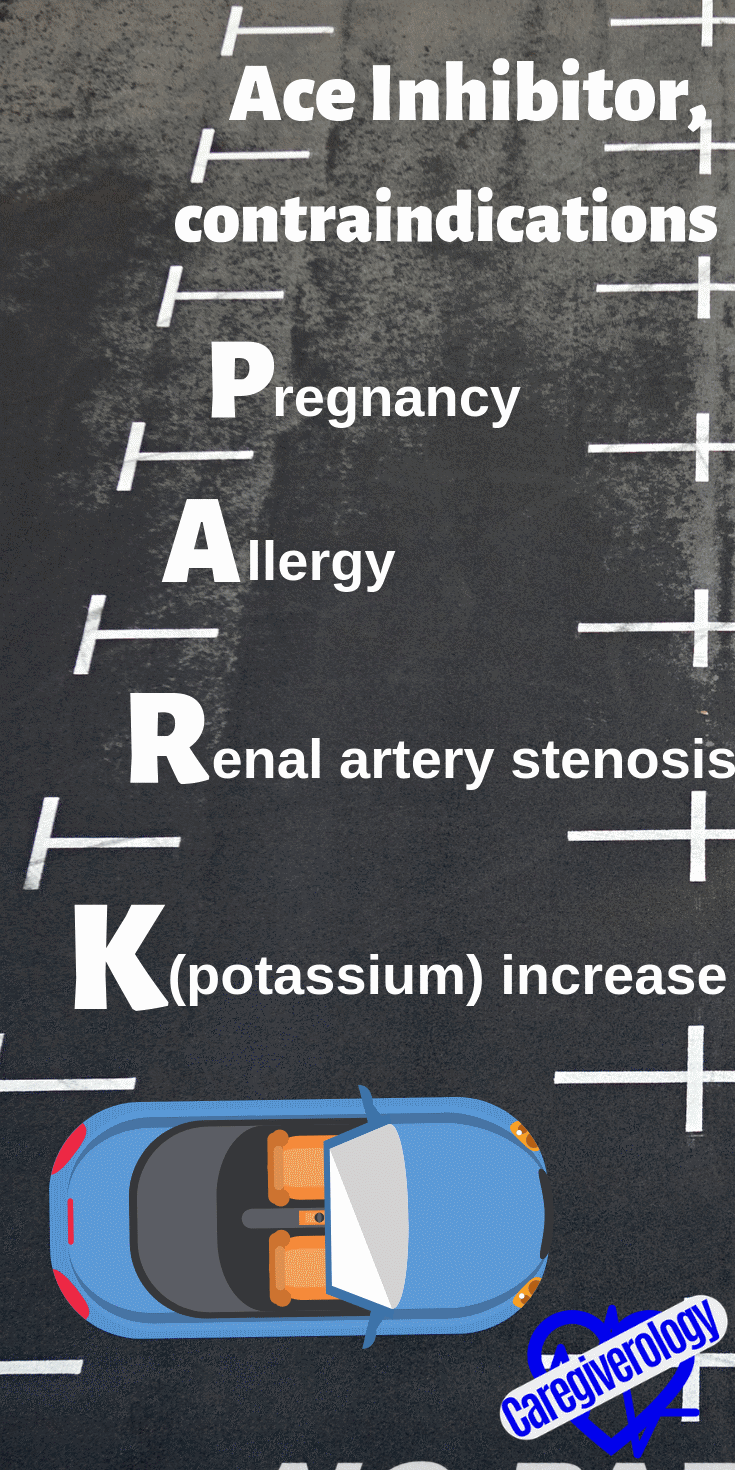
ACE Inhibitor, contraindications: PARK
Pregnancy
Allergy
Renal artery stenosis
K (potassium) increase: hyperkalemia
Activities of Daily Living (abbreviated as ADL), assessment: BATTED
Transfers
Eating
Dressing
Addison's Disease, clinical findings: FATIGuED
Fatigue
Antibodies (ie: anti-adrenal, antithyroid, antiparietal cell
Triad: hyponatremia, hypokalemia, azotemia
Increased pigmentation of skin and tongue
Gastrointestinal: weight loss, anorexia
Nausea and vomiting
Eosinophillia, neutropenia
Decreased blood pressure (ie: hypotension)
Alcoholism Screening Questions: CAGE
Have you ever tried to Cut down on your drinking?
Do people ever Anger you about your drinking?
Do you ever feel Guilty about your drinking?
Do you ever require an Eye opener (ie: drink of alcohol) to get going in the morning?
Aldosterone, regulation of secretion from adrenal cortex: RNAS
Renin-angiotensin mechanism
Na concentration in blood
ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide)
Stress
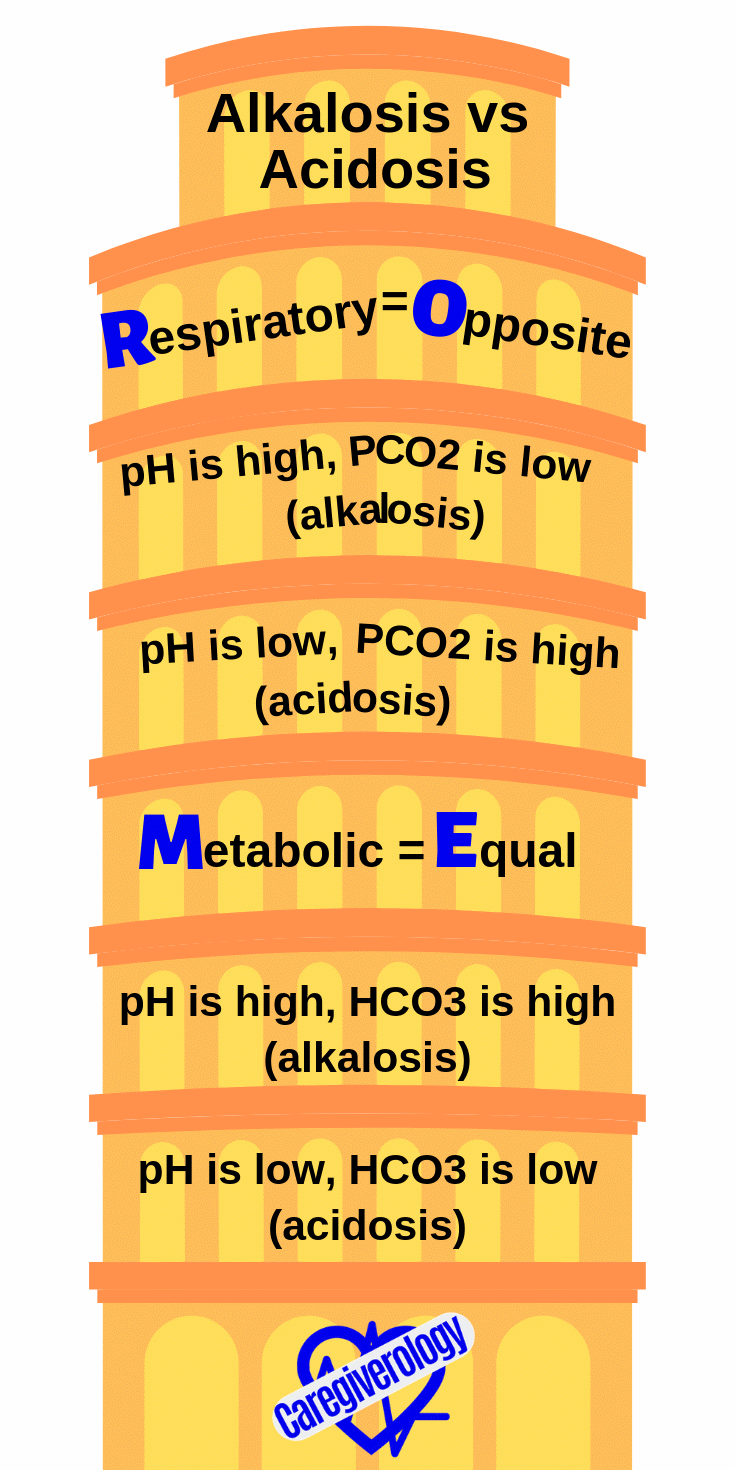
Alkalosis Vs Acidosis, directions of pH and HCO3: ROME
Respiratory=Opposite
pH is high, PCO2 is low (alkalosis)
pH is low, PCO2 is high (acidosis)
Metabolic=Equal
pH is high, HCO3 is high (alkalosis)
pH is low, HCO3 is low (acidosis)
Anal Pain, differential diagnosis: HHAAFF
Hemorrhoids
Hematoma
Abscess
Anal prolapse
Fistula
Fissure
Anemia, normocytic-normochromic, causes: CREAM PILE
Connective tissue disease
Renal disease
Endocrinopathy (ie: hypothyroidism, Addison's disease, hypopituitarism, hypoparathyroidism)
Amyloidosis
Pregnancy
Infectious (eg: abscess, subacute bacterial endocarditis)
Liver disease
Everything else (eg: malnutrition, malignancy)
Angina Pectoris, precipitants: 4 E's
Emotional upset
Exertion
Exposure to cold air
Eating large meal
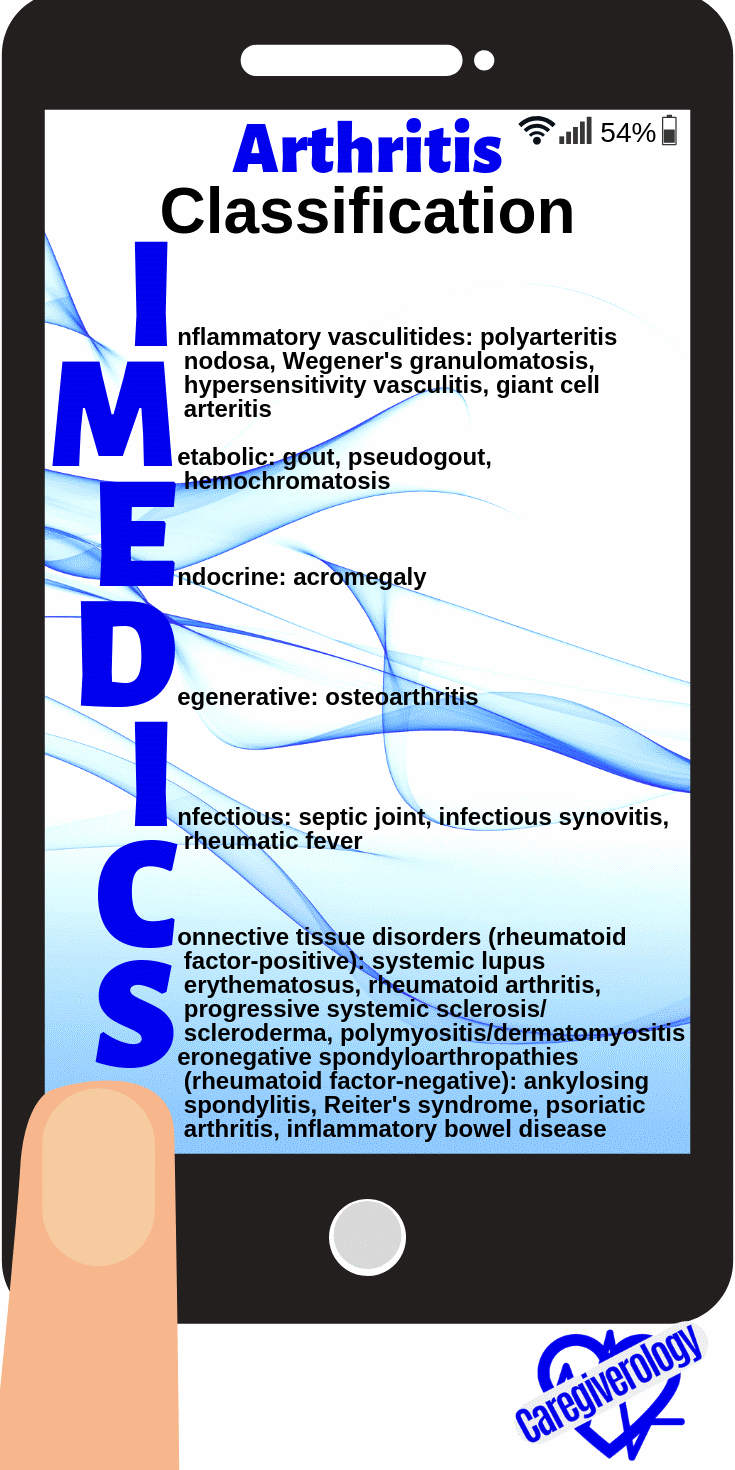
Arthritis, classification: IMEDICS
Inflammatory vasculitides: polyarteritis nodosa, Wegener's granulomatosis, hypersensitivity vasculitis, giant cell arteritis
Metabolic: gout, pseudogout, hemochromatosis
Endocrine: acromegaly
Degenerative: osteoarthritis
Infectious: septic joint, infectious synovitis, rheumatic fever
Connective tissue disorders (rheumatoid factor-positive): systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, progressive systemic sclerosis/scleroderma, polymyositis/dermatomyositis
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies (rheumatoid factor-negative): ankylosing spondylitis, Reiter's syndrome, psoriatic arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease
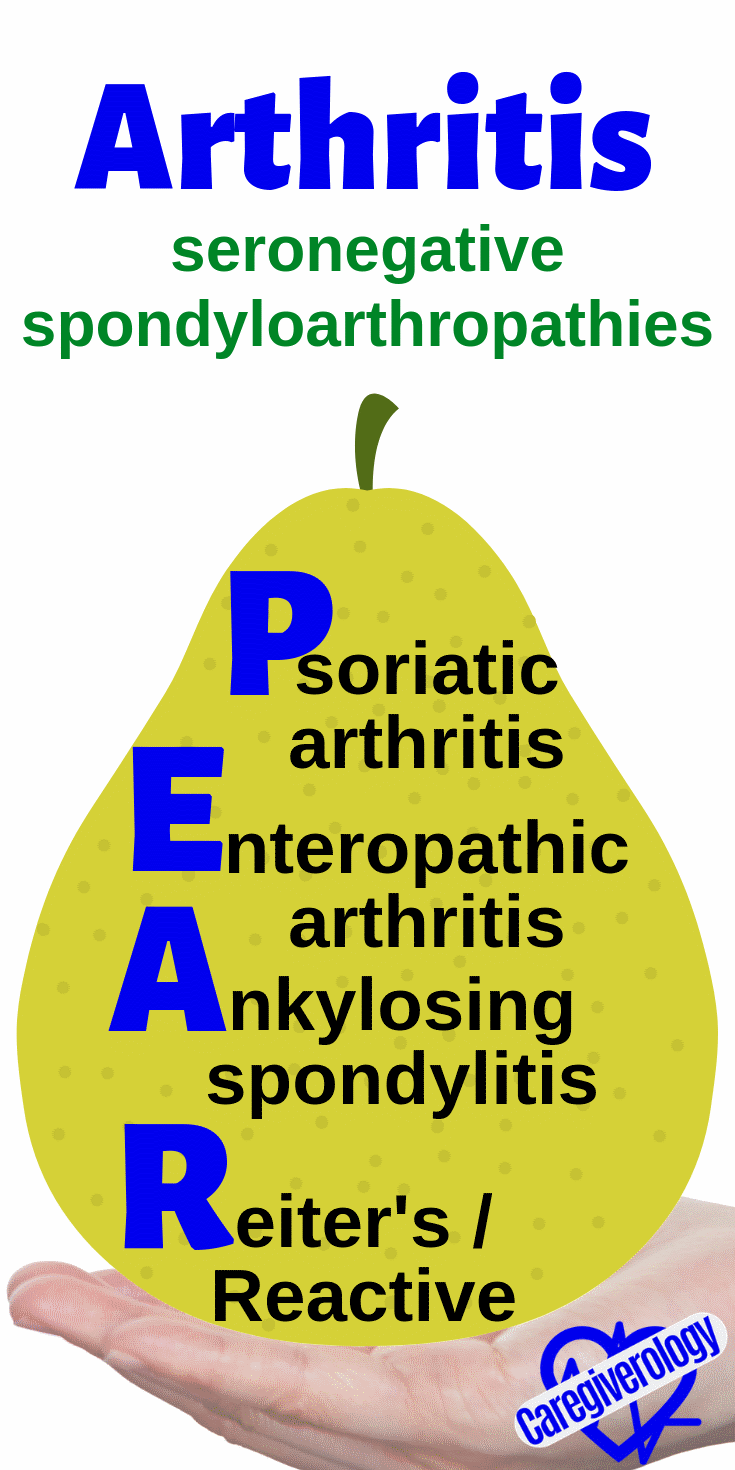
Arthritis, seronegative spondyloarthropathies: PEAR
Psoriatic arthritis
Enteropathic arthritis
Ankylosing spondylitis
Reiter's/Reactive
Ascites, causes: P^4
Peritonitis: peritoneal carcinomatosis, post-irradiation, peritoneal dialysis, pancreatitis, mesothelioma, bacterial, TB, fungal, parasitic
Peritoneal lymphatic obstruction: traumatic, congenital
Protein deficiency: cirrhosis, protein-losing enteropathy, nephrotic syndrome, kwashiorkor
Portal hypertension: pre-hepatic, hepatic, post-hepatic causes
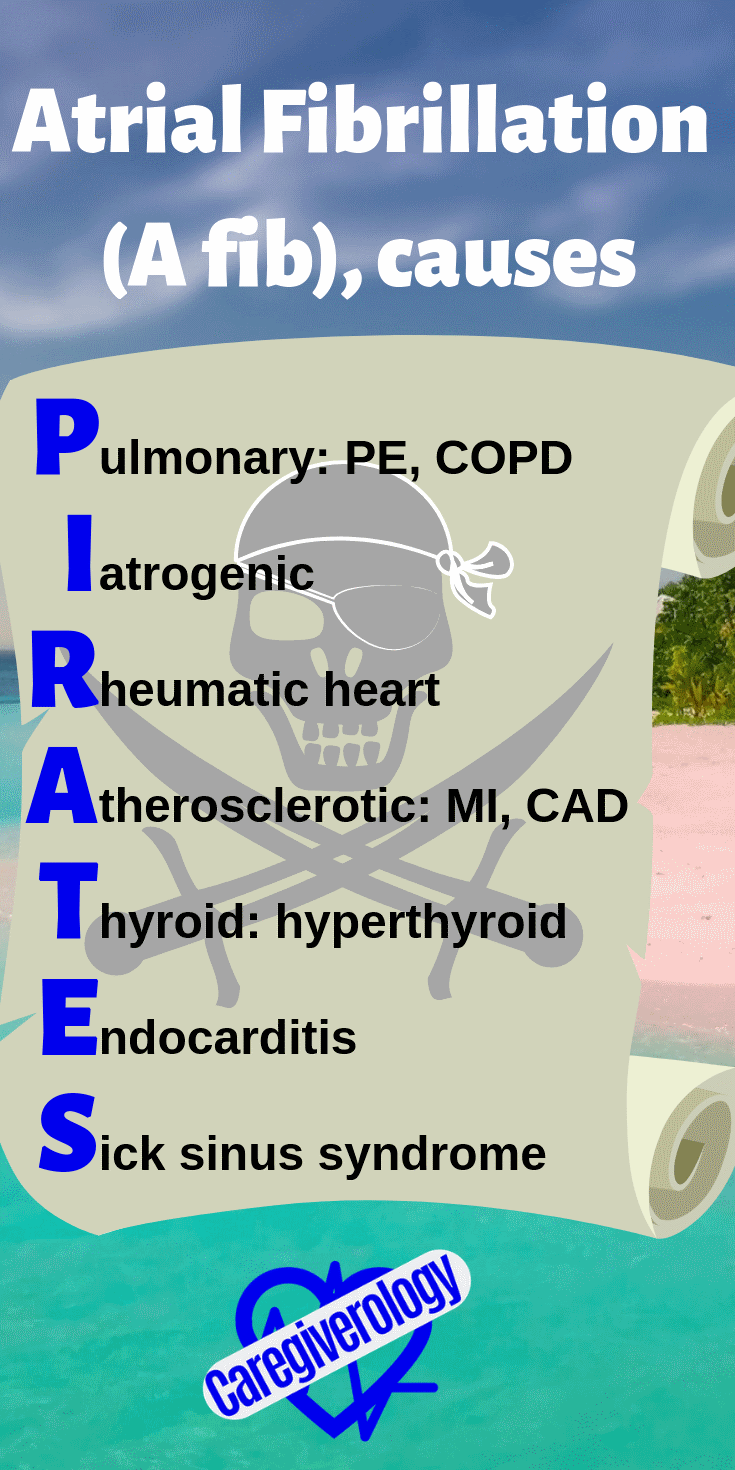
Atrial Fibrillation (A fib), causes: PIRATES
Pulmonary: PE, COPD
Iatrogenic
Rheumatic heart: mitral regurgitation
Atherosclerotic: MI, CAD
Thyroid: hyperthyroid
Endocarditis
Sick sinus syndrome
B
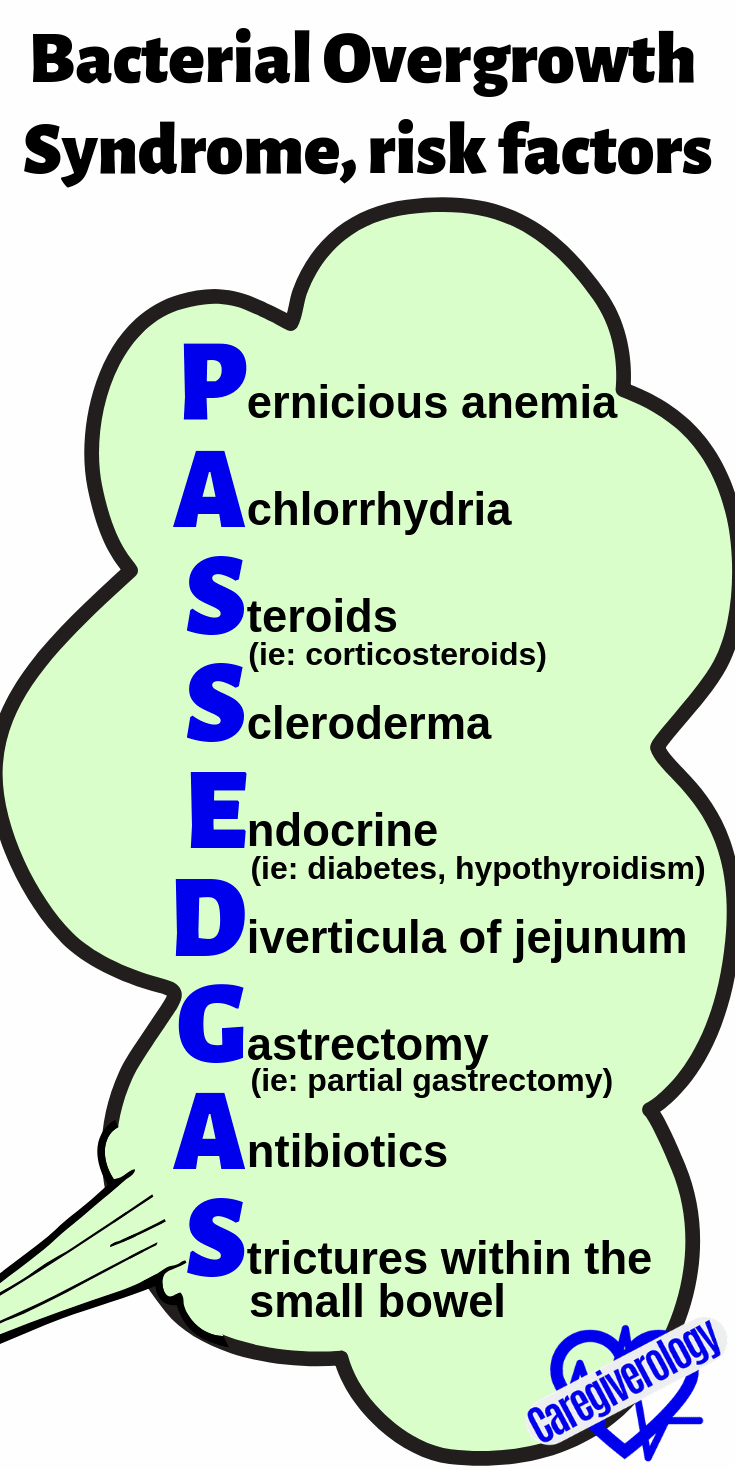
Bacterial Overgrowth Syndrome, risk factors: PASSED GAS
Pernicious anemia
Achlorrhydria
Steroids (ie: corticosteroids)
Scleroderma
Endocrine (ie: diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism)
Diverticula of jejunum
Gastrectomy (ie: partial gastrectomy)
Antibiotics
Strictures within the small bowel
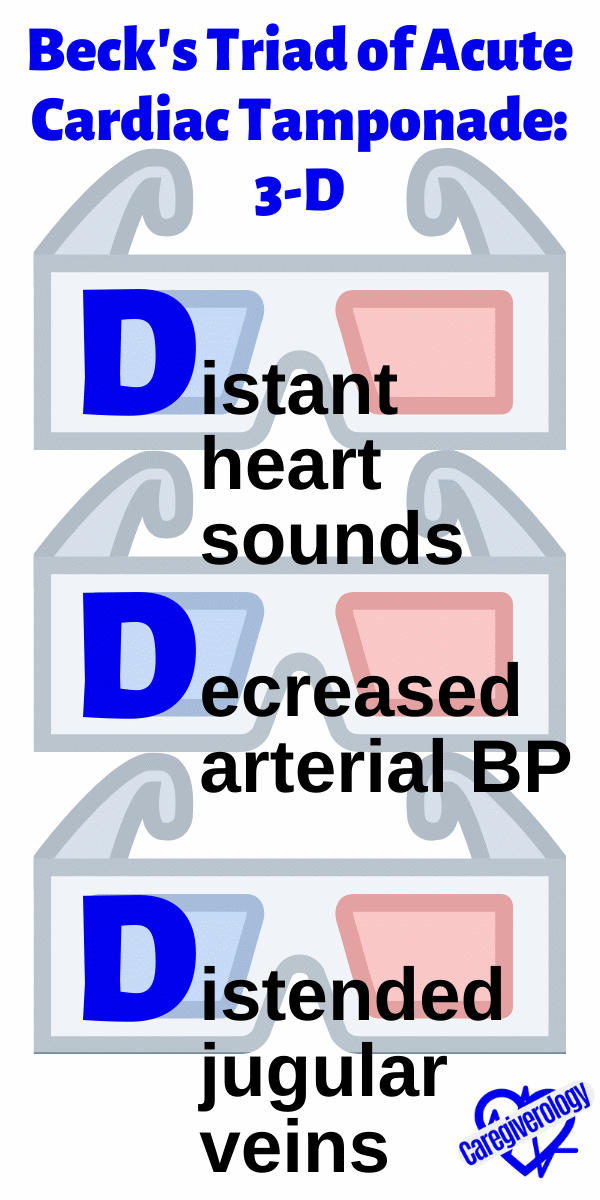
Beck's Triad of Acute Cardiac Tamponade: 3-D
Bloody Diarrhea, infectious causes: CESSYEC
Campylobacter jejuni
E coli (enterohemorrhagic strains)
Salmonella
Shigella
Yersinia enterocolytica
Entamoeba histolytica
Clostridium difficile (c diff)
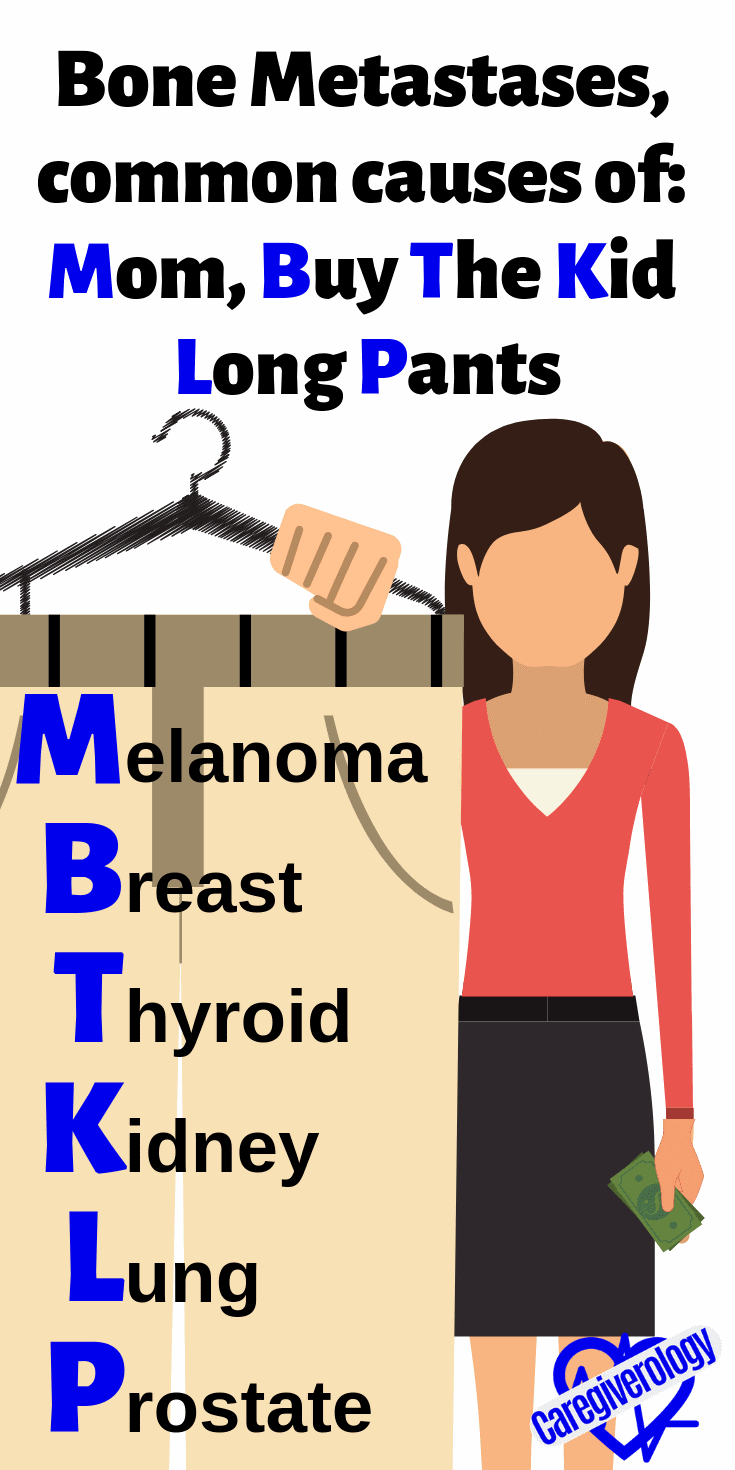
Bone Metastases, common causes of: Mom, Buy The Kid Long Pants
Malignant melanoma
Breast
Thyroid
Kidney
Lung
Prostate
Burns, initial resuscitation: SAVE A PATIeNT
Stop the burning process
ABCs of basic life support
Visualize the patient for all injuries
Estimate burn size and begin fluid resuscitation
Airway: intubate if inhalation injury present
Penicillin: start antibiotics
Analgesic
Topical therapy: flumazanine cream
Intoxicants/Inhalants
e
Nasogastric tube
Tetanus toxoid
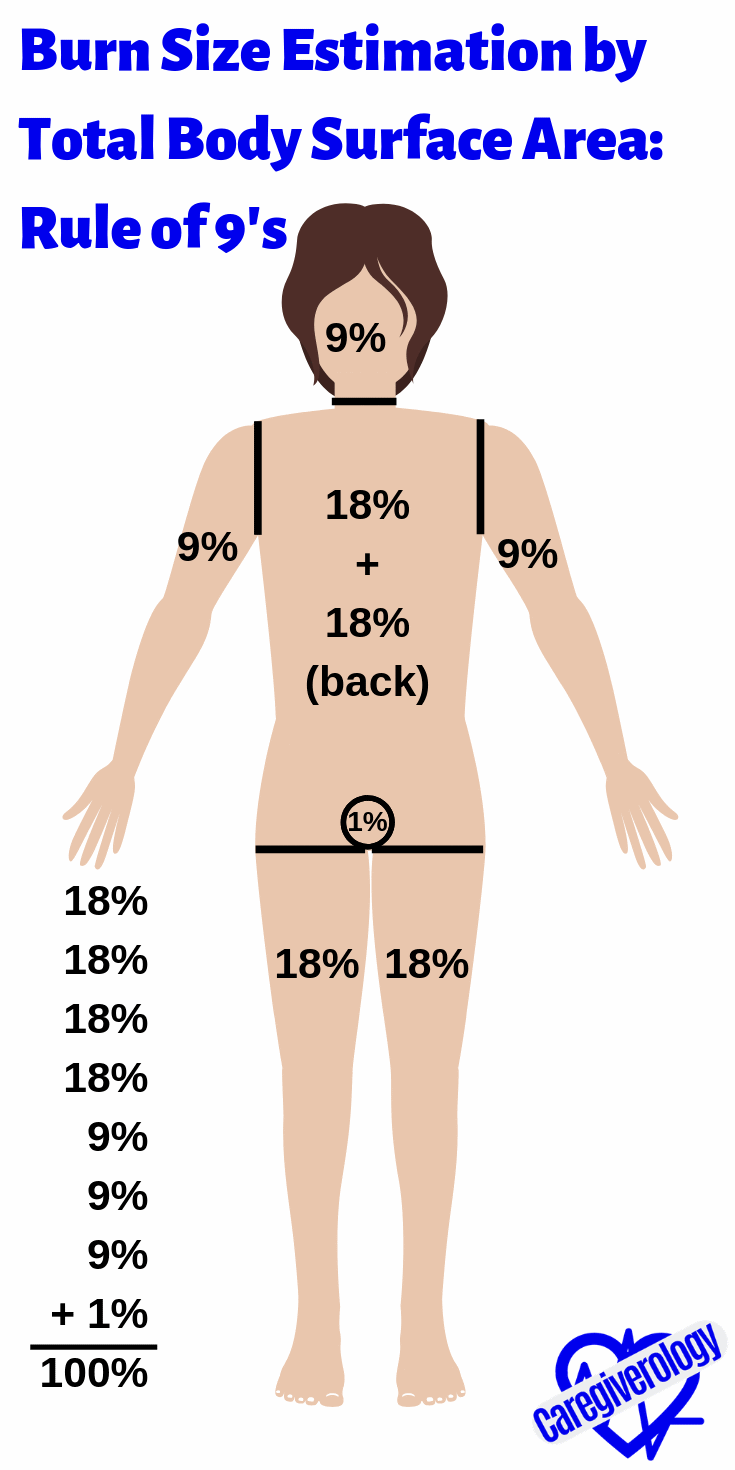
Burn Size Estimation by Total Body Surface Area: Rule of 9's
Entire head: 9%
Entire trunk: 18% + 18% = 36%
Entire arm: 9% + 9% = 18%
Entire leg: 18% + 18% = 36%
Whole body: 100%
C
Carcinogens, known types: AABBCC
Arsenic (causes skin cancer)
Asbestos (causes mesothelioma, laryngeal cancer)
Benzidine dye (causes bladder cancer)
Beta-naphthylamine (causes bladder cancer)
Chromium (causes nasal cancer)
Chloride vinyl (causes liver angiosarcoma)
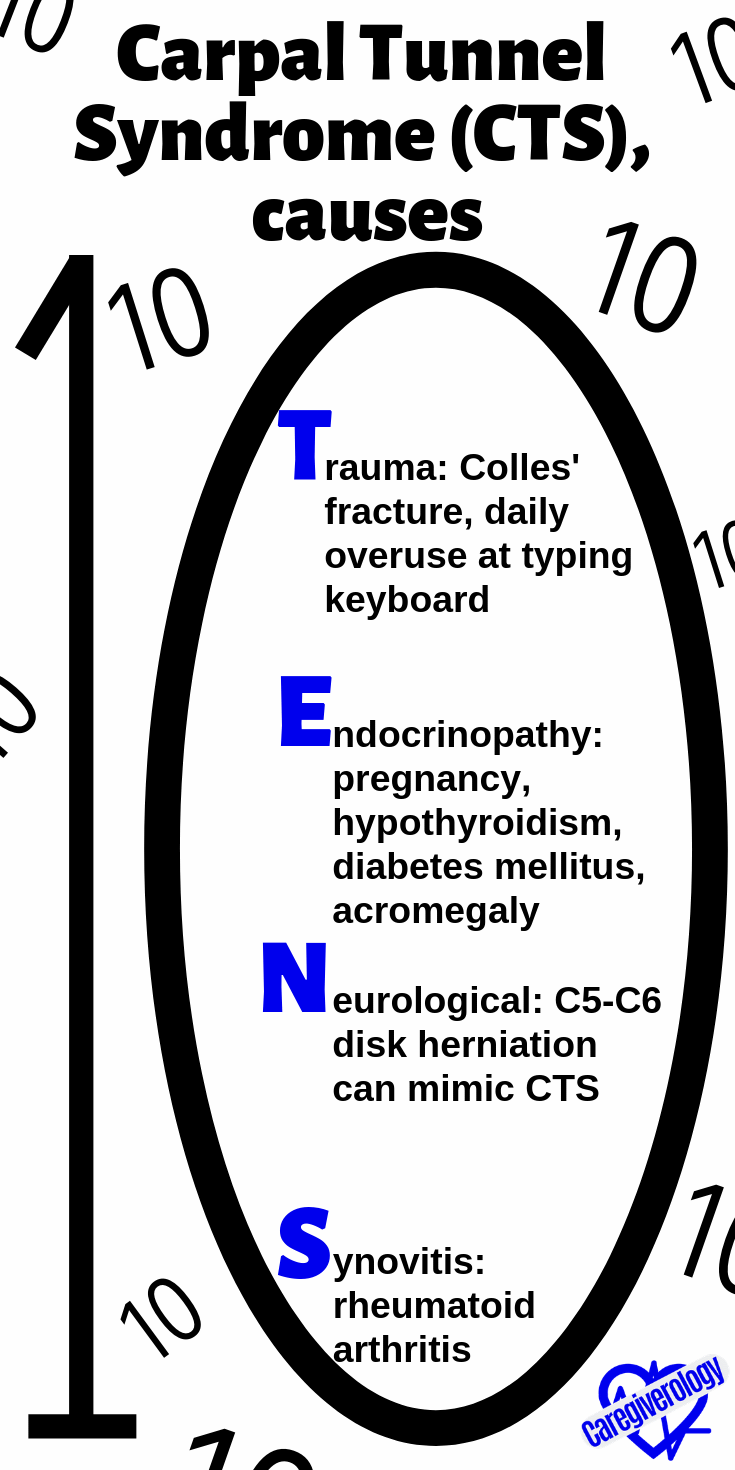
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), causes: TENS
Trauma: Colles' fracture, daily overuse at typing keyboard
Endocrinopathy: pregnancy, hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, acromegaly
Neurological: C5-C6 disk herniation can mimic CTS
Synovitis: rheumatoid arthritis
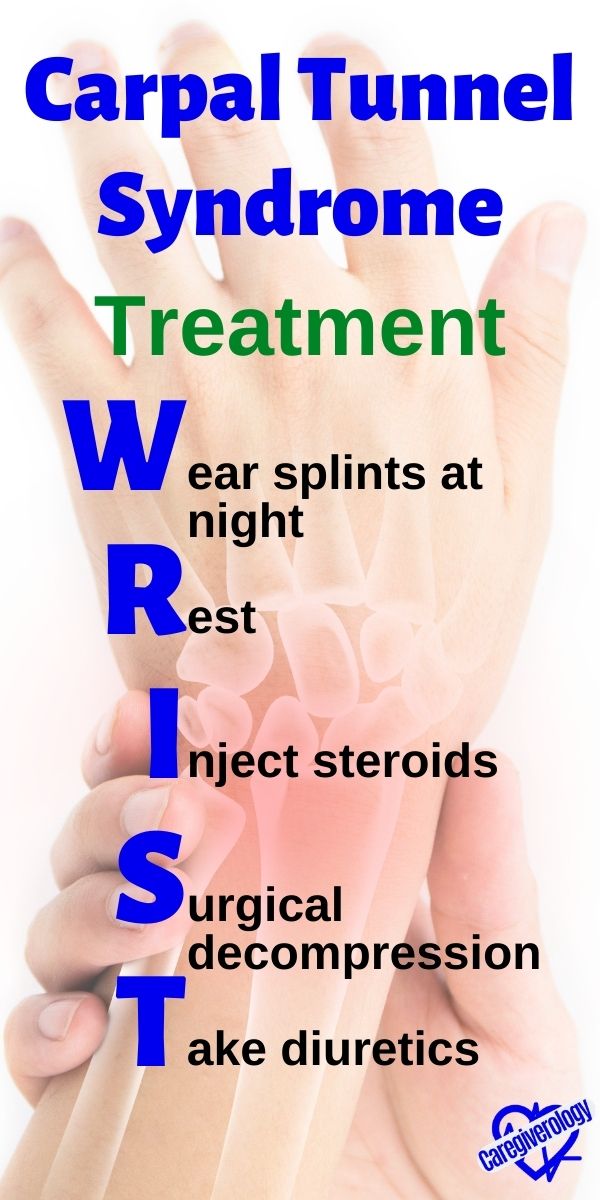
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, treatment: WRIST
Wear splints at night
Rest
Inject steroid
Surgical decompression
Take diuretics
Celiac Disease, Treatment/prevention: Elimination of gluten-containing foods (BROW) from the diet
Barley
Rye
Oats
Wheat
Cerebellar damage signs, DANISH
Dysdiadochokinesis
Ataxia
Nystagmus
Intention tremor
Slurred speech
Hypotonia
Cerebellar Lesion, signs: DDDARN It
Dysarthria
Dysdiadokokinesia
Dysmetria
Ataxia
Rebound phenomenon
Nystagmus
Intention tremor
Cerebral Palsy, criteria for diagnosis: POSTER
Posturing: especially abnormal extensor thrusting
Oropharyngeal problems: tongue thrusts, grimacing, swallowing difficulties
Strabismus
Tone increased or decreased in muscles
Evolutionary responses: persistent primitive reflexes or failure to develop equilibrium and protective responses
Reflexes: deep tendon reflexes are increased and plantar reflexes are up going
Cervical Spine X-ray, interpretation: ABCS
Alignment of: soft tissue, vertebral bones anteriorally, facet joints, spinous processes
Bone fractures
Cartilage: intervertebral disc spaces should be equal
Soft tissues: prevertebral and retropharyngeal spaces are increased with bony injury, blood, or air from tracheal injury
Colles' Fracture, casting position: PUP
Phlexion (ie: wrist flexion) +
Ulnar deviation of wrist +
Pronation of wrist
Compartment Syndrome (Ischemic Injury), signs: P^6
Passive stretching causes severe pain (moat reliable sign)
Pain
Pallor
Paresthesia
Poor capillary refill
Pulselessness (late sign)
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF), causes of exacerbation: FAILURE
Forgot medication
Arrhythmia/Anemia
Ischemia/Infarction/Infection
Lifestyle: consuming too much salt
Upregulation of cardiac output (CO): pregnancy, hyperthyroidism
Renal failure
Embolism: pulmonary
Constipation in Childhood, organic causes: HHHAND
Hirschprung's disease
Hypothyroidism
Hypercalcemia
Anal fissure
Neurogenic bowel: spina bifida
Diabetes mellitus
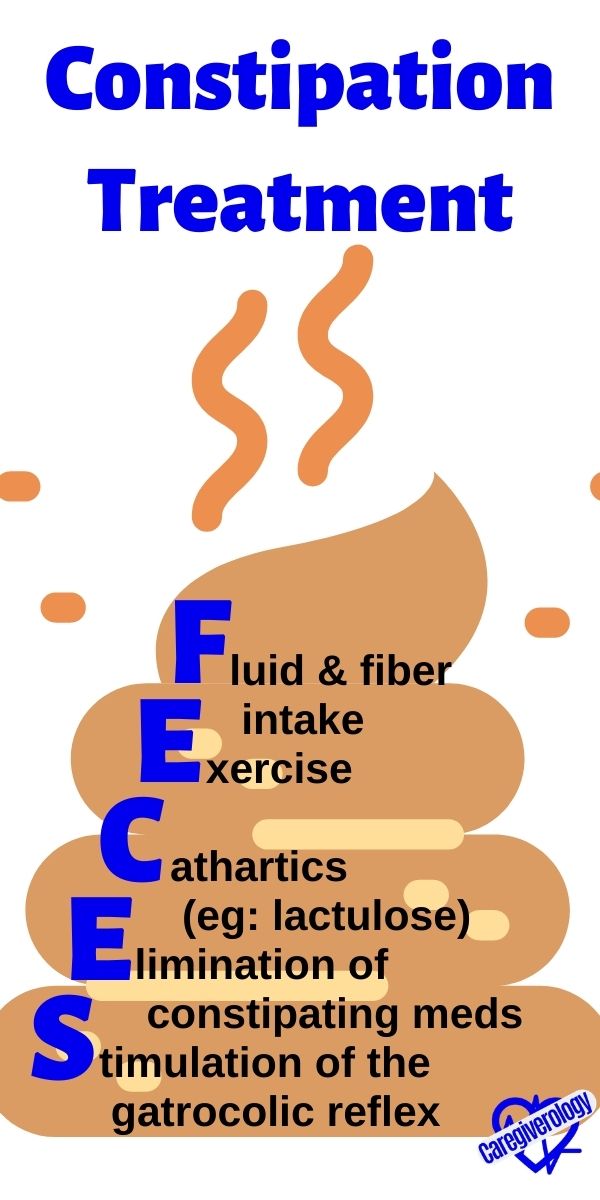
Constipation, treatment: FECES
Fluid and fiber intake
Exercise
Cathartics (eg: lactulose)
Elimination of constipating medications
Stimulation of the gatrocolic reflex (ie: enema)
Cough (chronic), differential: When cough in nursery, rock the "CRADLE"
Cystic fibrosis
Rings, slings, and airway things (tracheal rings)/Respiratory infections
Aspiration: swallowing dysfunction, tracheoesophageal (TE) fistula, gastroesophageal reflux
Dyskinetic cilia
Lung, airway, and vascular malformations: tracheomalacia, vocal cord dysfunction
Edema: heart failure
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, signs: B MAD
Blindness
Myoclonic movements of the limbs
Ataxia
Dementia: rapidly progressive in nature
Croup Scoring: Remain Calm Coughing Makes Stridor Appear
Retractions: none --> intercostal and nasal flaring
Color: normal --> central cyanosis
Cough: none --> paroxysmal "bark"
Mental status: alert --> restless --> delirious
Stridor: none --> stethoscope --> without stethoscope
Air entry: normal --> decreased --> delayed or minimal
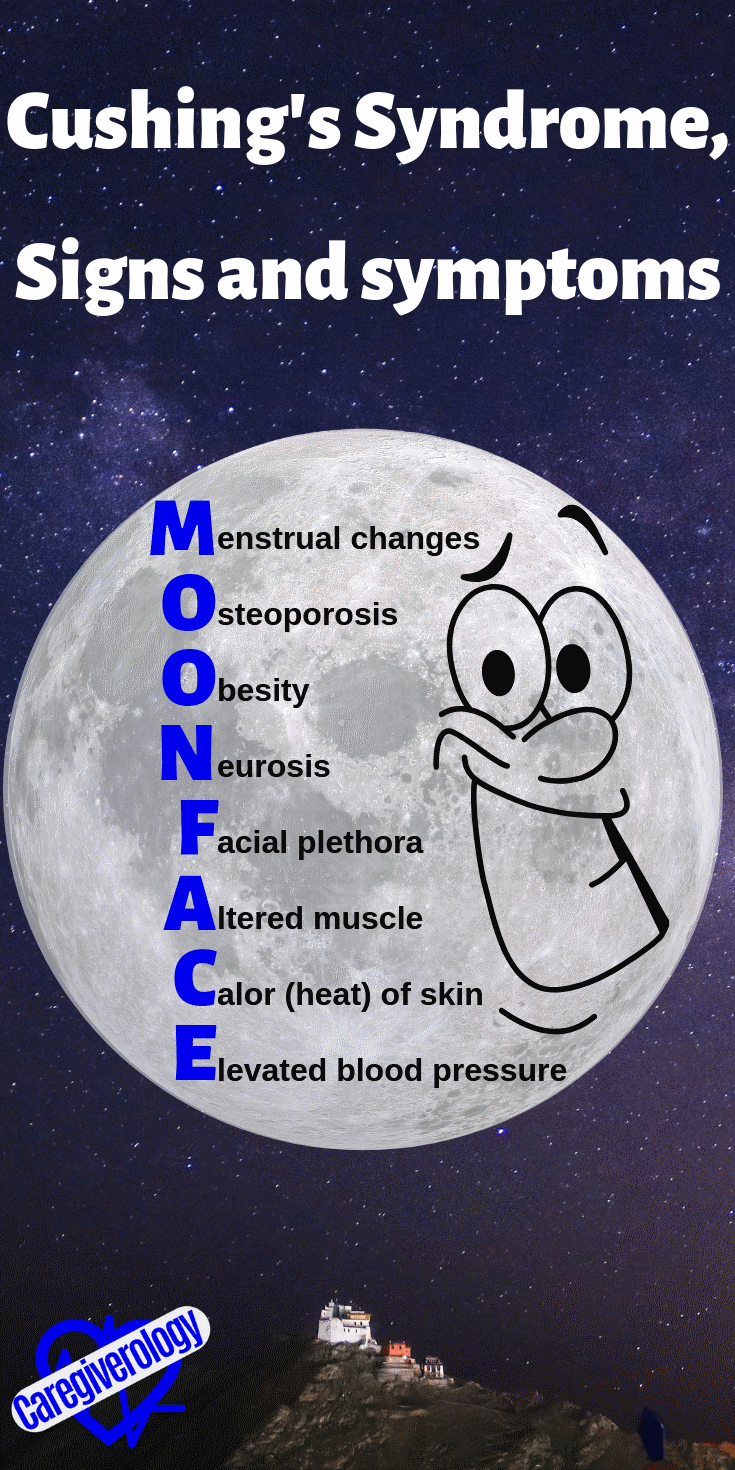
Cushing's Syndrome, Signs and symptoms: MOON FACE
Menstrual changes
Osteoporosis
Obesity
Neurosis
Facial plethora (moon face, hirsutism)
Altered muscle
Calor (heat) of skin
Elevated blood pressure
D
Delirium, signs: AIDS
Acute onset, then fluctuation over days
Inattentiveness: especially to conversation
Disorganized thinking: incoherent speech
State of consciousness either reduced or hypervigilant
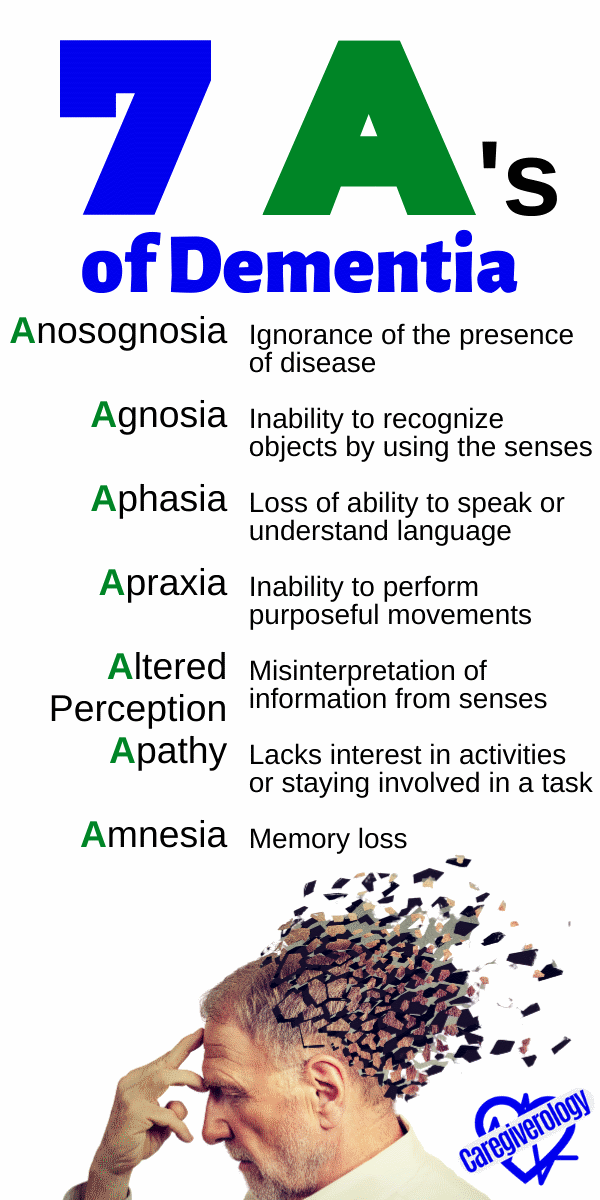
Dementia: 7 A's
Anosognosia - Ignorance of the presence of disease
Agnosia - Inability to recognize objects by using the senses
Aphasia - Loss of ability to speak or understand language
Apraxia - Inability to perform purposeful movements
Altered Perception - Misinterpretation of information from senses
Apathy - Lacks interest in activities or staying involved in a task
Amnesia - Memory loss
Dementia, Alzheimer's, differential diagnosis: DEMENTIAS
Drugs
Encephalitis
Metabolic: electrolyte or liver abnormality, dehydration, acute intermittent porphyria
Endocrine: thyroid disease, diabetes mellitus
Normal-pressure hydrocephalus
Trauma: chronic subdural hematoma
Infection: of lung or urine, AIDS, syphilis
Affective disorder: depression manifesting as pseudodementia
Structural defect of brain: infarction, tumor, abscess
Dementia Patient, management: FICSMA
Family answering questions, referral to services and resources, treatment of behavioral disturbances, helping with placement, postmortem investigation and support
Intellectual status: observing for/treating delirium, depression, drug side effects, incontinence: initiating discussion
Clinical investigation, retraining regimens
Sleep: counselling family regarding expected disorders, ruling out environmental and physical causes, treating insomnia
Mobility/Activity: investigating causes of immobility, adjusting environment and drugs, restricting wandering
Depression, 5 drugs causing it: PROMS
Propanolol
Reserpine
Oral contraceptives
Methyldopa
Steroids
Depression: major episode characteristics: SPACE DIGS
Sleep disruption
Psychomotor retardation
Appetite change
Concentration loss
Energy loss
Depressed mood
Interest wanes
Guilt
Suicidal tendencies
Depression, signs and symptoms: ASSESS PAT
Appetite diminished, weight loss
Sleep disturbance: especially diminished number of sleep hours
Sexual libido diminished
Energy diminished
Suicidality, Self-worthlessness, and guilt
Psychomotor agitation
Anhedonia
Thought process impaired
Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Precipitants of: In^5
Insulin deficiency
Infarction (ie: myocardial infarction)
Infection (eg: viral respiratory tract infection)
Injury (ie: trauma)
Infant (ie: pregnancy)
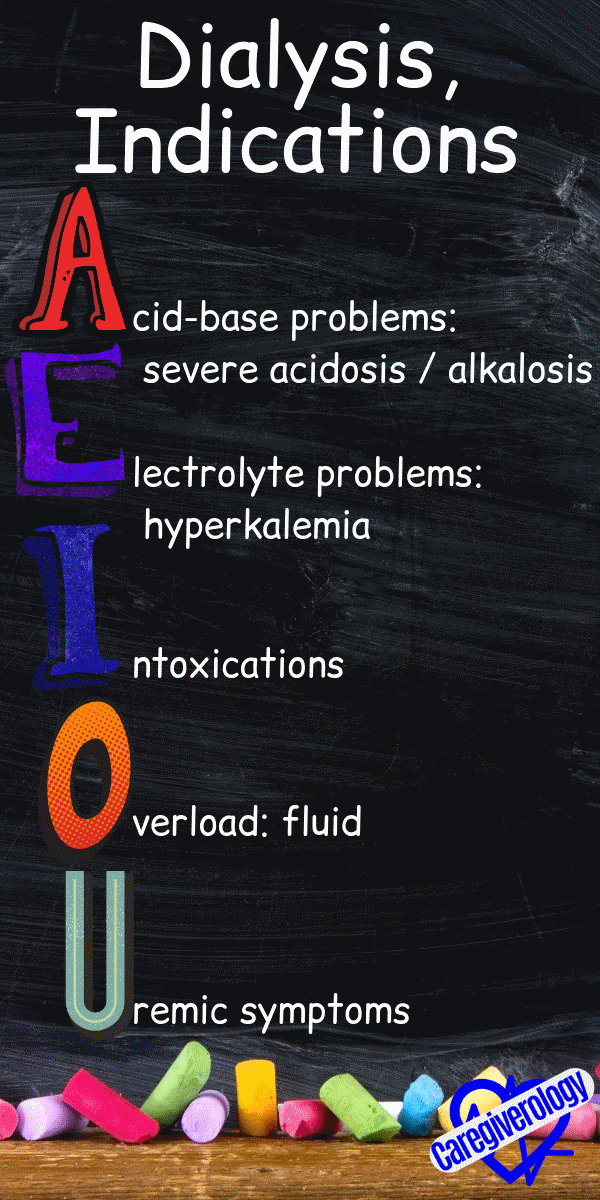
Dialysis, indications: AEIOU
Acid-base problems: severe acidosis or alkalosis
Electrolyte problems: hyperkalemia
Intoxications
Overload: fluid
Uremic symptoms
Digital (finger) Clubbing, causes: FINGER Clubb
Fibrosis of lung
Infections: lung abscess, bronchiectasis, infective endocarditis
Neoplastic: lung adenocarcinoma
Gastrointestinal: chronic liver disease, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease
Endocrine: hyperthyroidism
Renal disease: chronic
Cardiac: cyanotic congenital cardiac disease
lubb
Direct Sympathomimetic Catecholamines: DINED
Dopamine
Isoproterenol
Norepinephrine
Epinephrine
Dobutamine
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC), causes: TOM'S V
Trauma (especially brain trauma)
Obstetrical (ie: abruptio placenta, retained fetus, placenta previa, septic abortion)
Malignancy
Sepsis (eg: meningococcemia, E coli)
Venom (usually from viper snake bites)
Drug Toxicity/Overdose Blood Tests: A^6
Alcohols: ethanol, methanol, ethylene glycol
Aspirin
Acetaminophen
Anticonvulsants: phenytoin, phenobaribital
Antidepressants: tricyclics, lithium
Anxiolytics: benzodiazepines
Ducket John's major criteria: ACNES
Arthritis
Carditis
Nodule (subcutaneous)
Erythrema marginatum
Sydenham chorea
Duodenal Ulcer, indications for surgical management: I PROB
Intractable pain
Perforation
Refractive to medical treatment
Obstruction (ie: of the gastric outlet)
Bleeding
Dyspnea of Sudden-Onset, causes: MAAP^5S
Mucous plug
Asthma
Aspiration, respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)
Pulmonary embolus
Pneumonia
Pneumothorax
Pulmonary edema
Psychogenic
Sepsis
E
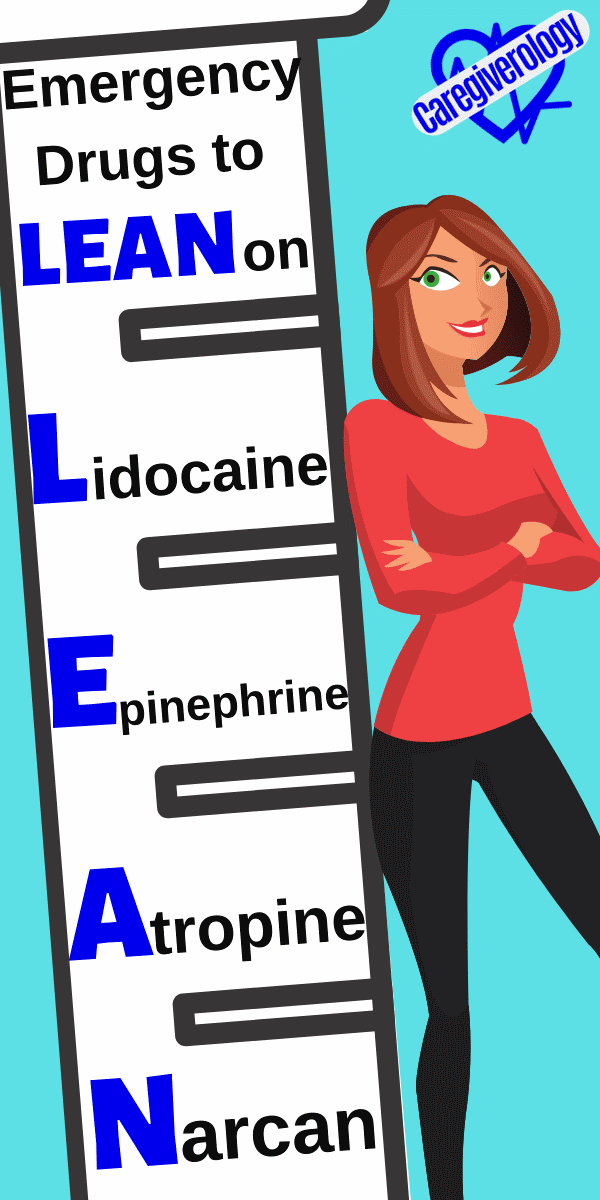
Emergency Drugs to LEAN on
Lidocaine
Epinephrine
Atropine
Narcan
Endocarditis, clinical manifestations: LIME
Local (ie: valvular vegetations, and destruction)
Immune complexes (ie: retinal Roth spots, renal lesions, Janeway lesions, Osler's nodes)
Metastatic lesions (ie: bacterial "mycotic" aneurysms)
Embolisms (ie: splenic, cerebral, renal, and adrenal infarcts)
Endometrial Carcinoma, risk factors: HONDA
Hypertension
Obesity
Nulliparity
Diabetes
Age: increased
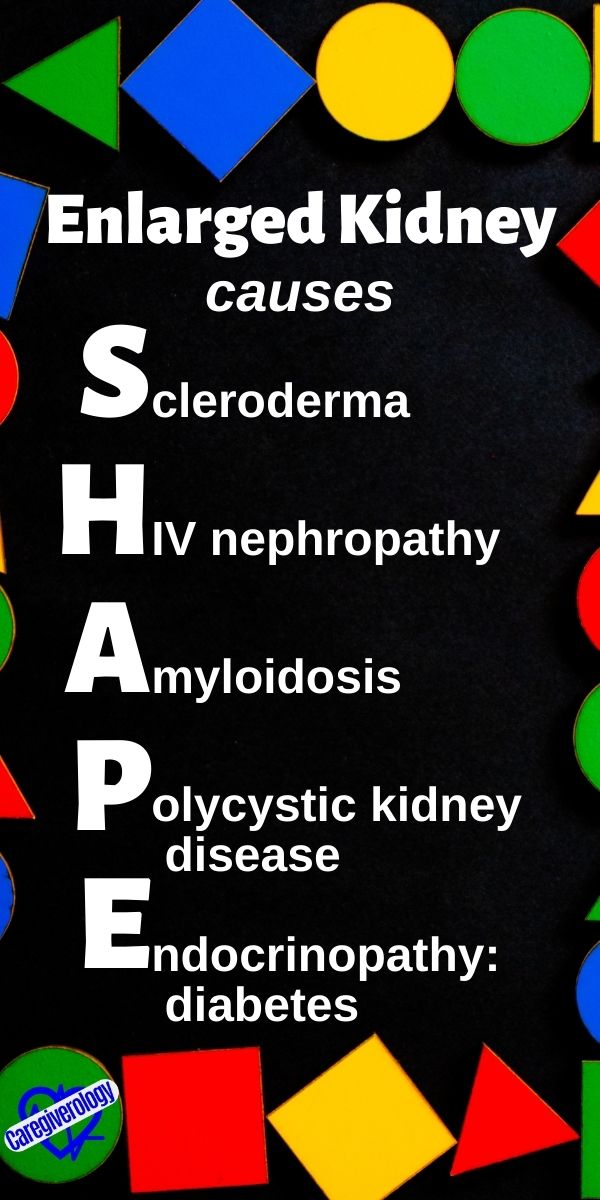
Enlarged Kidneys, causes: SHAPE
Scleroderma
HIV nephropathy
Amyloidosis
Polycystic kidney disease
Endocrinopathy: diabetes
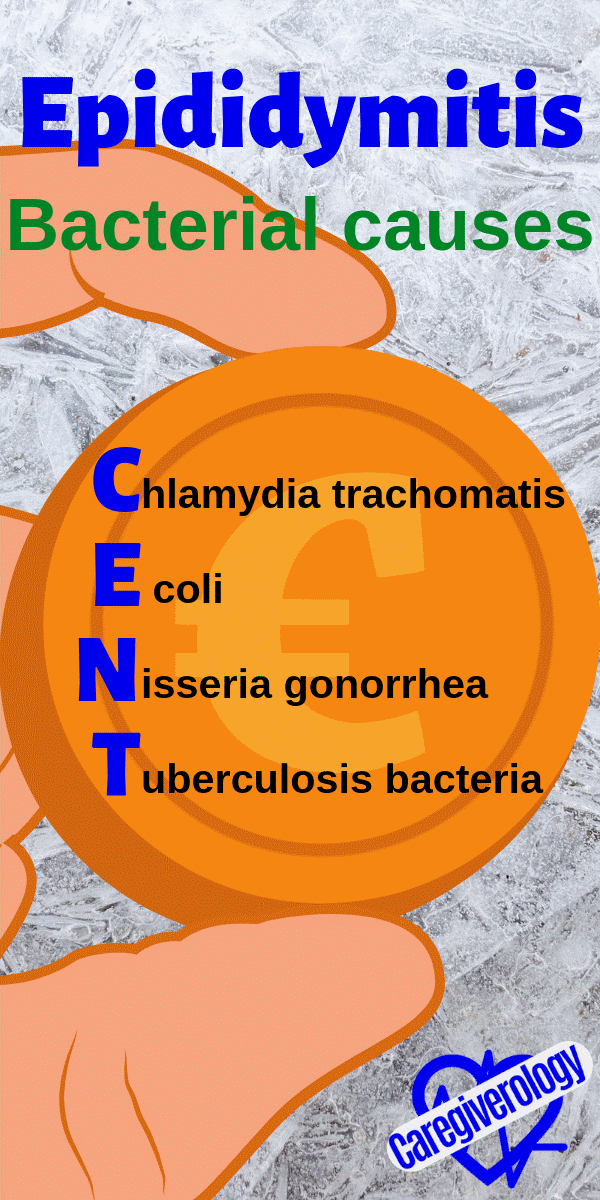
Epididymitis, bacterial causes: CENT
Chlamydia trachomatis
E coli
Nisseria gonorrhea
Tuberculosis bacteria
Epiglottitis, signs and symptoms: 5 D's
Distressed
Drooling
Dysphagia
Dysphonia
Dyspnea
Epiphyseal injury, Salter-Harris classification: SALTEr
Type 1: Straight through the epiphyseal growth plate
Type 2: Above the epiphyseal growth plate: in a fragment of metaphysis attached to the epiphysis
Type 3: Lower: through and below the epiphyseal growth plate
Type 4: Through the epiphysis and metaphysis
Type 5: Emergency: crush of the epiphyseal growth plate
Exposures to Infectious Agents, diagnosis: COASTED
Contacts: family, friends, co-workers
Oral ingestion: seafood, restaurants, picnics
Animal exposure: pets, wild animals
Sexual history: sexual orientation, number of partners, use of prostitutes
Travel history
Employment exposure: animals, insects, fumes
Drug history: illicit drugs, needle sharing, over-the-counter medications
F
Failure to Thrive, causes: 7 C's
Congenital abnormalities: ventricular septal defect
Chromosomal abnormalities: Down's syndrome
Cystic fibrosis (CF)
Celiac disease
Cow's milk protein intolerance: allergy
Calorie-protein malnutrition
Cruelty: parental neglect, abuse, environmental deprivation
Felty's Syndrome Components: SANTA
Splenomegaly
Anemia
Neutropenia
Thrombocytopenia
Arthritis
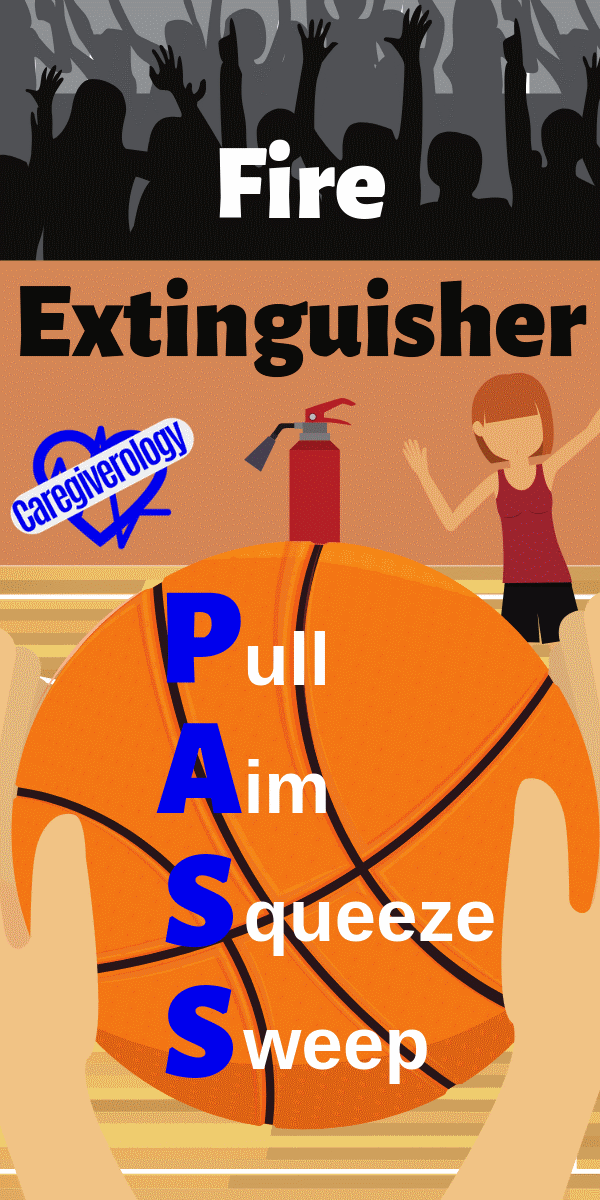
Fire Extinguisher: PASS
Pull
Aim
Squeeze
Sweep
Fire Response Plan: RACE
Rescue
Alarm
Confine
Extinguish/Evacuate
G
Gallstone Disease, risk factors: CHOlesterol PIGment
Cirrhosis of liver
Hemolysis
Obesity
lesterol
Parity >2
Indian (ie: North American Indian)
Gender (ie: female, fair, fat, forty, flatulent, and fertile)
ment
Gastric Carcinoma, risk factors: A^5
Anemia (ie: pernicious anemia)
Achlorrhydria
Atrophic gastritis
Adenomas (ie: gastric adenomas)
A blood type
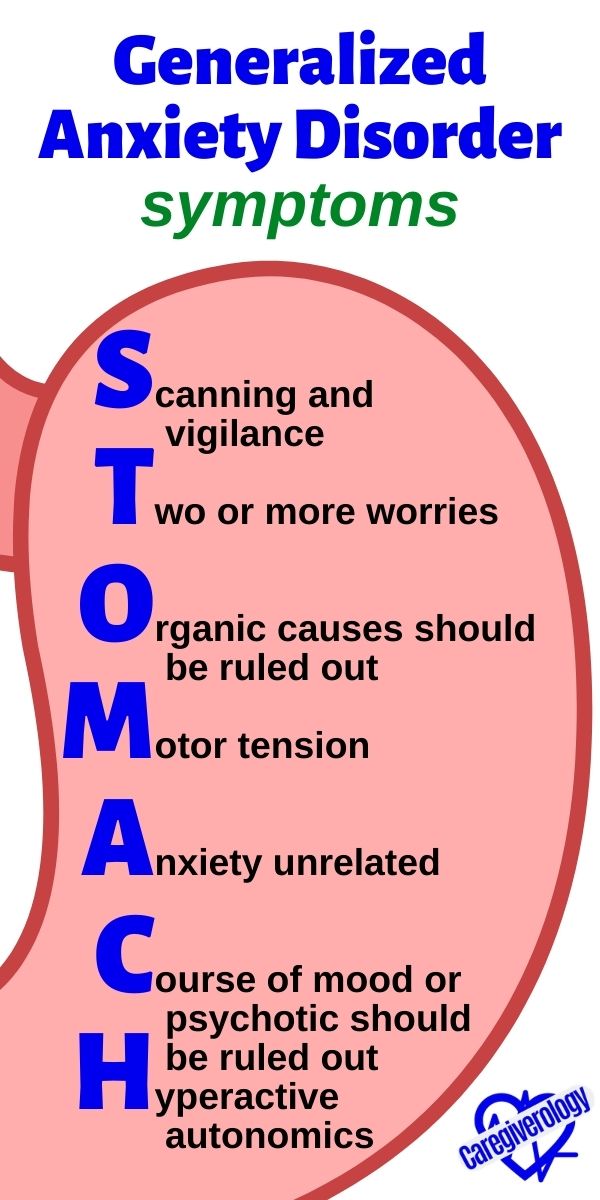
Generalized Anxiety Disorder, symptoms: STOMACH
Scanning and vigilance
Two or more worries
Organic causes should be ruled out
Motor tension
Anxiety unrelated
Course of mood or psychotic should be ruled out
Hyperactive autonomics
Glomerulonephritis in childhood: HIS PISH
Henoch-Schonlein purpura
IgA nephropathy (ie: Berger's disease)
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
Immune vasculitis (eg: Wegener's granulomatosis, polyarteritis nodosa)
Subacute bacterial endocarditis
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome
Graves' Ophthalmopathy, Clinical characteristics: PREDNISOL
Proptosis
Retraction of eyelids (Dairymple's sign)
Edema (periorbital)
Diplopia
Neuropathy of optic tract (leads to poor visual acuity
Inhibited upward gaze
Skin changes (eg: pretibial myxedema, peu d'orange)
Onset ages 20-40
Lid lag on downward gaze (Graefe's sign)
H
Headache, classification: VITAMIN
Vascular: migraine, cluster, toxic vascular, hypertensive
Inflammatory and Traction: mass lesion (tumor, edema, hematoma, hemorrhage), arteritis, phlebitis, neuralgia, occlusive vascular disease, temperomandibular joint syndrome
Atypical variants
Muscle contraction headache: depressive equivalents and conversion reactions, cervical osteoarthritis, chronic myositis
Infectious: meningitis, encephalitis
Non-cranial sources: eyes, ears, nose, throat, teeth
Hematuria, causes: SITTTG
Stones: kidney stone
Infection: urinary tract infection
Tuberculosis
Trauma
Tumor: renal or bladder cancer
Glomerulonephritis
Hemochromatosis, clinical manifestations: ABCDEFG
Arthralgias
Bronzed skin color
Cardiac: enlargement, heart failure, conduction abnormalities
Diabetes
Early in life: aged mid-30's upon presentation
Ferritin (serum) elevated
Gonadal involvement: decreased libido, infertility
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura, signs and symptoms: RASHH
Rash: purpuric rash over buttocks, estensor surfaces of legs, pre-tibial region
Arthralgia
Sore abdomen
Hematuria
Hematochezia
Hepatic Encephalopathy, signs and symptoms: SCALP
Sychosis
Confusion
Asterixis
Lethargy --> coma: late sign
Personality changes: early sign
HLA-B27 associated diseases: PAIR
Psoriasis
Ankylosing spondylitis
Inflammatory bowel disease
Reiter's syndrome
Hodgkin's Disease, clinical features: WAAARM LIFHS
Weight loss
Anemia
Abdominal pain
Alcohol-induced pain in lymph nodes
Regional lymphadenopathy
Mediastinal involvement (eg: compression of local structures)
Lymphadenopathy
Itchiness
Fever, night sweats, Pel-Epstein fever
Hyperuricemia (eg: manifesting as gout)
Splenomegaly
Hourly Rounding: 4 P's
Pain - “How is your pain?”
Position - “Are you comfortable?”
Potty - “Do you need to use the bathroom?”
Possessions - “Do you need me to move the phone, call light, trash can, water or your bedside table within reach?”
Hydrocephalus in Infants and Children, causes: MHO
Meningitis: infectious
Hemorrhage: periventricular hemorrhage
Obstruction: aqueduct stenosis, tumor
Hypercalcemia, Causes: SHIFT
Sarcoidosis (and other granulomatous diseases)
Hyperparathyroidism, hyperthyroidism
Immobilization
Familial
Tumor, thiazides (others: lithium, vitamin D)
Hypercalcemia, Causes: SIR
Skeletal resorption enhanced: hyperparathyroidism (usually due to a single parathyroid adenoma), malignancy (eg: bronchial carcinoma), hyperthyroidism, immobilization
Intestinal absorption enhanced: granulomatous disease (eg: tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, vitamin D intoxication
Renal excretion reduced: diuretic ingestion
Hyperkalemia, Signs and symptoms: MURDER
Muscle weakness
Urine (oliguria, anuria)
Respiratory distress
Decrease cardiac contractility
ECG changes
Reflexes (hyperreflexia, areflexia)
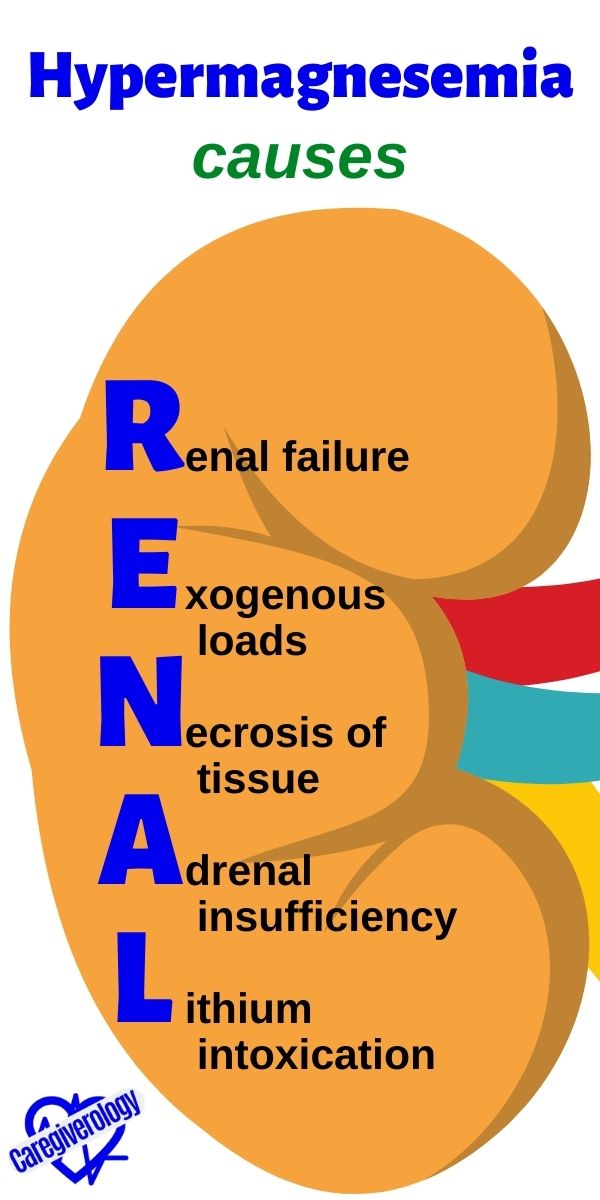
Hypermagnesemia, Causes: RENAL
Renal failure
Exogenous loads (eg: MgSO4, magnesium-containing antacids)
Necrosis of tissue (eg: burns)
Adrenal insufficiency
Lithium intoxication
Hypertension (HTN), Effects on organs: HIgHER PEa
Heart (ie: left ventricular hypertrophy, angina, myocardial infarction)
Infarction in brain
g
Hemorrhage in brain
Encephalopathy
Renal disease (eg: glomerulosclerosis)
Peripheral vascular disease
Eyes (ie: arteriolar narrowing, retinal hemorrhages and exudates, papilledema)
a
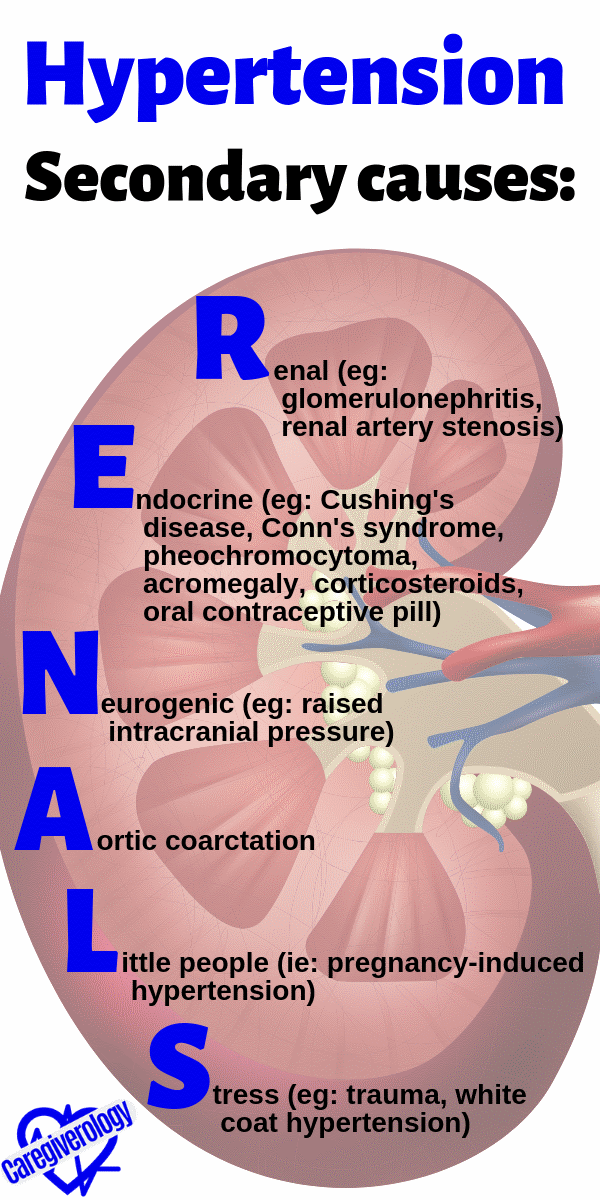
Hypertension, Secondary causes: RENALS
Renal (eg: glomerulonephritis, renal artery stenosis)
Endocrine (eg: Cushing's disease, Conn's syndrome, pheochromocytoma, acromegaly, corticosteroids, oral contraceptive pill)
Neurogenic (eg: raised intracranial pressure)
Aortic coarctation
Little people (ie: pregnancy-induced hypertension)
Stress (eg: trauma, white coat hypertension)
Hypertension, Treatment: ABCDE
ACE inhibitors
Beta-blockers
Calcium-channel blockers
Diuretics
Exercise, weight loss, and dietary modifications (try first)
Hyperthyroidism, Symptoms of: SWEATING
Sweating
Weight loss
Emotional lability
Appetite is increased
Tremor/ Tachycardia due to AF
Intolerance to heat/ Irritability
Nervousness
Goiter/ GI problems (diarrhea)
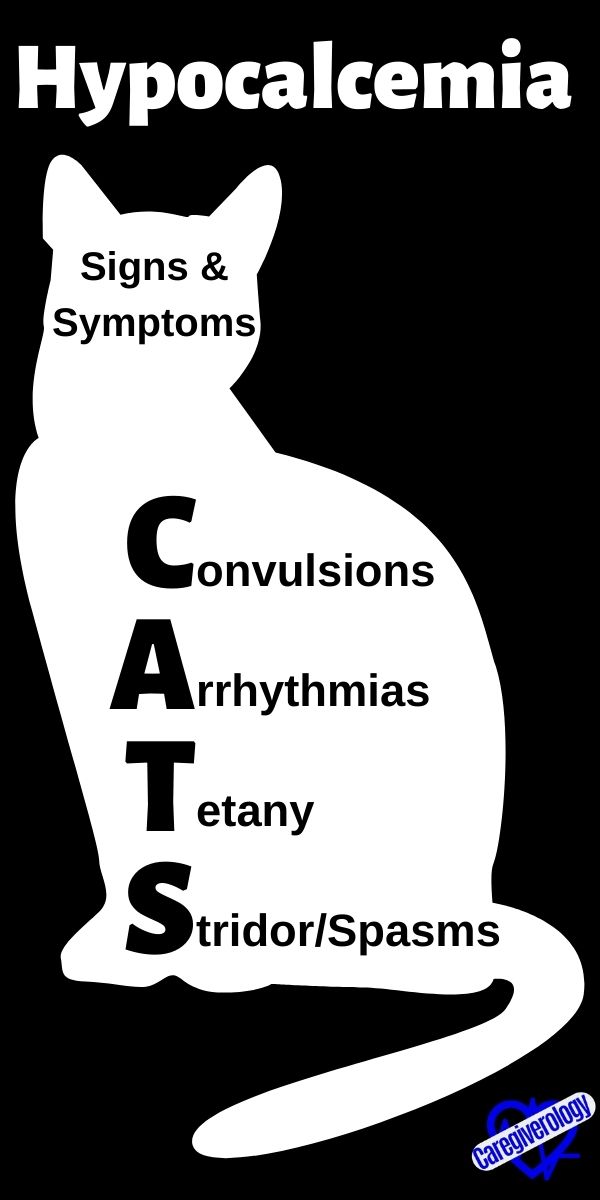
Hypocalcemia, Signs and symptoms: CATS
Convulsions
Arrhythmias
Tetany
Stridor/Spasms
Hypoglycemia, Causes: ExPLAIN
Exogenous: insulin, oral hypoglycemic agents, ethanol, and ASA excess
Pituitary insufficiency
Liver failure
Adrenal insufficiency (eg: Addison's disease)
Immune (ie: anti-insulin antibodies)
Neoplastic (eg: insulinoma, sarcoma, mesothelioma)
Hypoglycemia, Symptoms: TIRED
Tachycardia
Irritability
Restlessness
Excessive hunger
Diaphoresis
Hypomagnesemia, Causes: 10 Ds
Diarrhea and gastrointestinal losses
Diuretics and renal losses
Diabetes mellitus and endocrine causes
Dietary insufficiency
Diverted to free fatty acids
Drugs (eg: cisplatin, amphotericin B, diuretics)
Drinking excess amounts of ethanol
Delivery with toxemia during pregnancy
Decompensated heart, lungs, or liver
Denuded skin (eg: burns)
Hypothyroidism: Symptoms of: MOM'S SO TIRED
Memory loss
Obesity
Malar flush/ Menorrhagia
Slowness
Skin and hair become dry
Onset is gradual
Tired
Intolerance to cold
Raised blood pressure
Energy levels are low
Depressed
I
Impotence, causes: PLANE
Psychogenic: performance anxiety
Libido: decreased with androgen deficiency, drugs
Autonomic neuropathy: impede blood flow redirection
Nitric oxide deficiency: impaired synthesis, decreased blood pressure
Erectile reserve: can't maintain an erection
Incontinence, causes of transient form: DIAPERS
Delirium
Infection of urinary tract
Atrophic urethritis
Pharmacologic agents
Endocrine: glycosuria
Restricted mobility: "geographic incontinence" of new setting
Inflammatory Bowel Disease, extra-intestinal manifestations: STiNGSS
Sclerosing choangitis
Thromboembolic disease
i
Nephrolithiasis (ie: calcium oxalate, urate stones)
Skin (ie: aphthous ulcers, pyoderma gangrenosum, erythema nodosum)
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies
Iron Overdose, signs and symptoms: HIS HeP
Hemorrhagic gastroenteritis: 30-60 minutes post-ingestion
Improvement: appears improved 2-12 hours post-ingestion
Shock: 12-48 hours post-ingestion
Hepatic damage with possible hepatic failure: late
e
Pyloric stenosis: residual complication
J
Joint Pain, causes: SOFTER TISSUE
Sepsis
Osteoarthritis
Fractures
Tendon/muscle
Epiphyseal
Referred
Tumor
Ischemia
Seropositive arthritides
Seronegative arthritides
Urate
Extra-articular rheumatism: polymylagia
K
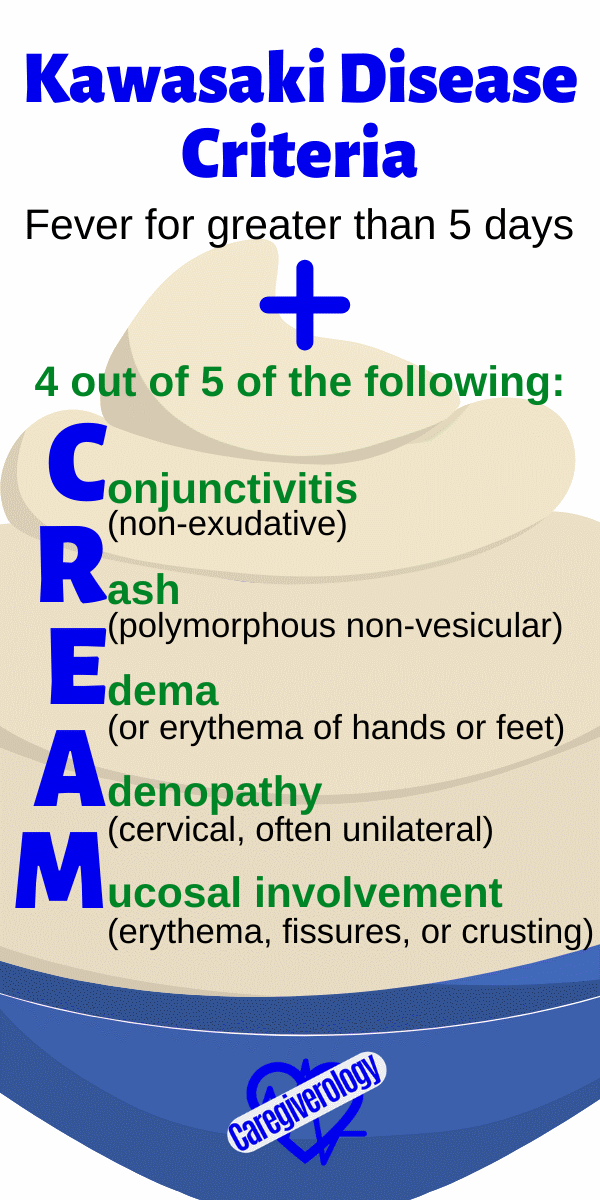
Kawasaki Disease Criteria: CREAM
Fever for greater than 5 days + 4 out of 5 of the following:
Conjunctivitis (non-exudative)
Rash (polymorphous non-vesicular)
Edema (or erythema of hands or feet)
Adenopathy (cervical, often unilateral)
Mucosal involvement (erythema, fissures, or crusting)
L
Laparotomy, emergency indications: PERFS
Peritonitis
Evisceration
Ruptured ectopic pregnancy
Free air in peritoneal cavity
Shock, with blood from rectum, nasogastric tube, or bladder
Lead Poisoning, Clinical manifestations: CRACK
Central nervous system (CNS): headache, memory loss, personality changes, encephalopathy
Reproductive: abortion, stillbirth
Anemia: microcytic
Colic: "lead colic" abdominal pain
Kidney: proximal tubular damage, interstitial fibrosis
Lithium, side effects: VANISH LITHHH
Vertigo
Ataxia
Nystagmus
Intention tremor
Stupor
Hyperreflexia
Leukocytosis
Insipidus: nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
T-wave inversion on the electrocardiogram (EKG)
Heaviness: weight gain
Hypothyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism
Lupus, drug-induced causes: CHIMP
Chorpromazine
Hydralazine
Isoniazid
Methyldopa
Procainamide
M
Malignant Melanoma, Diagnostic characteristics: ABCD
Asymmetry of lesion
Border irregularity
Color variegation
Diameter greater than 6 mm
Mania, symptoms: GREAT SAD
Grandiosity
Racing thoughts
Euphoria
Activities, goal-directed
Talkative
Sleep deprived
Activities, reckless
Distractibility
Megacolon, causes C^5
Congenital megacolon: Hirshprung's disease
Colitis: Chron's disease and ulcerative colitis
Cancer of the bowel
Chagas' disease: Trypanosoma cruzi destroy the bowel plexus
Crazy: functional megacolon
Mental Status Examination: COMO ESTAS
Cognitive function: calculation, concentration, insight, judgment
Overview: appearance, attitude, level of consciousness (LOC), movements
Memory: recent and remote
Orientation: to person, place, and time
Emotion: affect and mood
Speech: fluency, form, and comprehension
Thought: process, content, and perceptual disturbances
Attention: abstract thinking, recall, and intelligence
Something else: that might be important to the patient
Metabolic Acidosis, causes: USED CARP
Ureteroenterostomy
Saline hydration
Endocrinopathies: hyperparathyroid, hyperthyroid, Addison's
Diarrhea/DKA/Drugs
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Ammonium chloride
Renal tubular acidosis
Parenteral nutrition/pancreatic fistula
Metabolism Enzyme Inducers: Randy's Black Car Goes Putt Putt and Smokes
Rifampin
Barbiturates
Carbamazepine
Grisoefulvivn
Phenytoin
Phenobarb
Smoking cigarettes
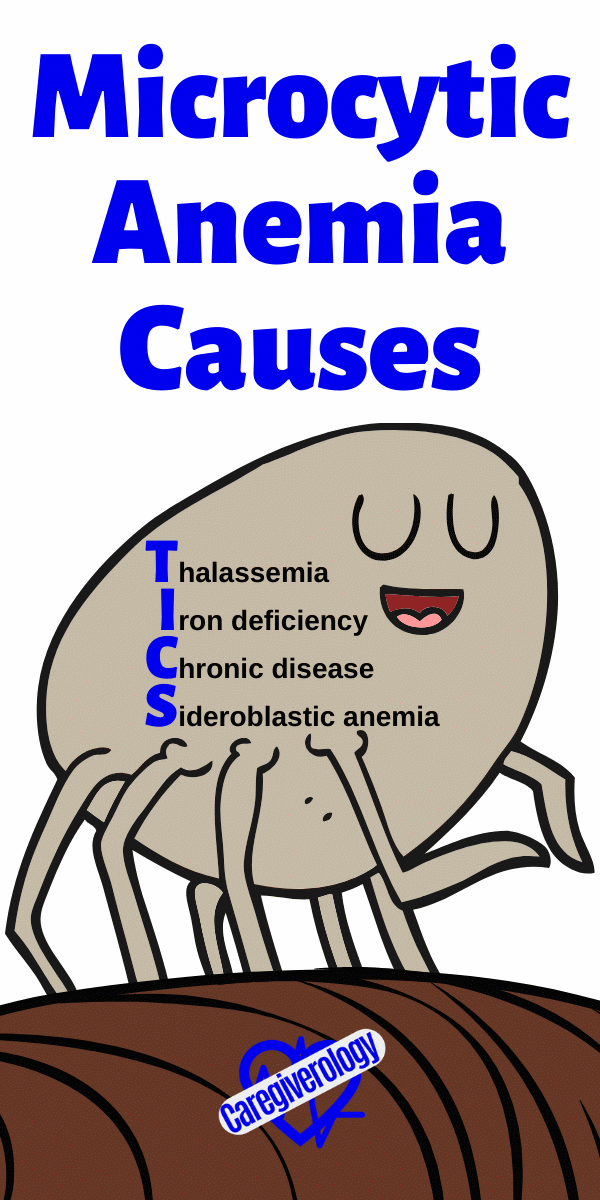
Microcytic Anemia Causes: TICS
Thalassemia
Iron deficiency
Chronic disease
Sideroblastic anemia
Migraine Headache, precipitating factors: C^6
Cino: wine
Cheese
Chocolate
Citrus fruits
Coronary vasodilator: nitrates
Contraceptive pill
Migraine Headache, symptoms: PUPIL
Pulsatile quality
Unilateral location
Physical activity worsens headache
Inhibits daily activity when present
Location: temporal region of head
Multiple Myeloma, signs and symptoms: POOR FAB
Pathological bone fractures
Osteoporosis
Osteolytic bone lesions on x-ray
Renal insufficiency or failure
Fatigue
Anemia
Bone pain
Myeloproliferative Disorders, clinical and laboratory features: PEPTIC
Pruritus
Ecchymoses
Peptic ulcer disease
Thrombosis
Increased blood levels of: uric acid, LDH, B12, histamine, eosinophils, basophils
Causes: chronic myelogenous leukemia, polycythemia rubra vera, thrombocythemia, myelofibrosis
Myocardial Infarction, Complications of: DARTH VADER
Death
Arrythmia
Rupture
Tamponade
Heart failure
Valve disease
Aneurism of ventricle
Dressler's syndrome
Embolism
Recurrence
Myocardial Infarction, Medical management: ABCDE
Aspirin
Beta-blocker
Coagulation (ie: thrombolytic; add heparin for anterior MI)
Dilator (ie: ACE inhibitor)
Elevated lipids (measure fasting lipids within 48 hours of admission, and start a statin agent if total cholesterol or LDL are elevated)
Myocardial Infarction (MI), Signs and symptoms: PULSE
Persistent chest pain
Upset stomach
Lightheadedness
Shortness of breath
Excessive sweating
Myocardial Infarction, Therapeutic treatment: O BATMAN!
Beta blocker
Aspirin
Thrombolytics (eg: heparin)
Morphine
ACE inhibitor PRN
Nitroglycerin
Myopia, clinical characteristics: LMMN
Long eyeball is...
Myopic, requiring...
Minus diopter lens for correction, and the patient is...
Nearsighted
N
Nephritic Syndrome with Decreased Complement Levels, causes: LESS Complement
Lupus
Endocarditis
Shunt infection-associated disease
Streptococcal glomerulonephritis
Cryoglobulinemia
Nicotine Effects: MTWTF (days of the week)
Mydriasis/Muscle cramps
Tachycardia
Weakness
Twitching
Hypertension/Hyperglycemia
Fasiculation
O
Obesity in Childhood, complications: FATSO
Furunculosis
Acanthosis nigricans
Triad (1. diabetes mellitus, 2. atherosclerosis, 3. hypertension)
Slipped femoral capital epiphysis
Obesity in adulthood
Occupational Lung Disease, Classification: ASTHMA
Asthma
Silicosis
Toxic gases
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (ie: extrinsic allergic alveolitis)
Many others
Asbestosis
Oral Contraceptive Pill, absolute contraindications to its use: OCP H^3
Oestrogen-dependent tumors (eg: hepatocellular carcinoma and adenoma, uterine carcinoma, breast carcinoma)
Cardiovascular disorders (ie: thromboembolic, cerebrovascular and coronary artery disease, and moderate to severe hypertension)
Pregnancy
Hepatic disease
Hyperlipidemia
Hemorrhage from vagina not yet diagnosed
Osteoarthritis, radiological features: OSSSteo
Osteophytes
Subchondral sclerosis
Subchondral cysts
Space between joint diminished
teo
Osteoporosis, Causes: COLLES FRACture
Congenital (eg: osteoporosis imperfecta, Ehlers-Danlos, homocysteinuria)
Osteoporosis type 1 (post-menopausal) and type 2 (senile)
Leukemia and other malignancies (eg: multiple myeloma)
Liver disease
Endocrine disease (eg: hyperparathyroidism, hyperthyroidism, acromegaly, Cushing's syndrome, hypogonadism, diabetes mellitus)
Steroids (ie: corticosteroids)
Familial
Renal disease
Anticonvulsants (eg: phenytoin)
Calcium deficiency (eg: malabsorption)
Osteoporosis Treatment: ABCDE
Activity and exercise
Biphosphonate drugs
Calcium supplementation (eg: 1000 mg/day)
D: vitamin D supplement
Estrogens: for post-menopausal women
Otalgia (Earache), causes of referred Pain: 10 T's
Teeth
Temporomandibular joint syndrome
Trismus
Trachea
Tube: eustachian tube
Tic douloureux: trigeminal neuralgia
Tonsilar: tonsillitis, cancer
Tongue
Throat: laryngeal carcinoma
Thyroiditis
Ovarian Carcinoma, types: MEGS-GEMS
Metastatic tumors: Krukenberg gastrointestinal, breast, endometrial, lymphoma
Epithelial tumors: serous, mucinous, endometrioid, clear cell, undifferentiated, Brenner's
Germ cells tumors: dysgerminoma, immature teratoma
Sex cord stromal tumors: granulosa cell, Sertoli-Leydig cell, thecoma
P
Pain History Checklist: CHLORIDE
CHaracter: stabbing, throbbing, etc
Location
Onset
Radiation
Intensity
Duration
Exacerbating and alleviating factors
Pain History Checklist: LOST WAR
Location
Onset
Severity
Time
Worsening factors
Alleviating factors
Radiation
Pancreatitis (Acute), Causes: IGETSMASHED
Idiopathic
Gallstones
Ethanol
Trauma
Steroids
Mumps
Autoimmune (PAN)
Scorpion stings
Hyperlipidemia/ Hypercalcemia
ERCP
Drugs
Papillary Necrosis Causes: SODA
Sickle cell
Obstructive pyelonephritis
Diabetes
Analgesics
Parkinsonism, drugs: SALAD
Selegiline
Anticholinergics: trihexyphenidyl, benzhexol, ophenadrine
L-Dopa and peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor: carbidopa, benserazide
Amantadine
Dopamine postsynaptic receptor antagonists: bromocriptine, lisuride, pergolide
Parkinsonism, essential features: TRAPS
Tremor: resting tremor
Rigidity
Akinesia
Postural changes: stooped
Stare: serpentine stare
Patient Examination Organization: SOAP
Subjective: what the patient says
Objective: what the examiner observes
Assessment: what the examiner thinks is going on
Plan: what they intend to do about it
Patient Profile (PP): LADDERS
Living situation/Lifestyle
Anxiety
Depression
Daily activities: describe a typical day
Environmental risks/Exposure
Relationships
Support system/Stress
Pelvic Mass That is Painful, differential diagnosis: CREAM PEA
Cyst (ie: ovarian cyst)
Renal colic
Ectopic pregnancy
Adhesions
Many other causes
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Endometriosis
Appendicitis/appendicial abscess
Penile Pain, differential diagnosis: P^8
Priapism
Phimosis
Paraphimosis
Peyronie's disease
Penile tumor
Purulence: venereal disease
Prostatitis
Push: coitus-related trauma/overuse
Pepsin-producing cells: chief of Pepsi-Cola
Chief cells of stomach produce Pepsin
Peripheral Polyneuropathy, causes: MMIIDD
Metabolic: diabetes mellitus, amyloidosis, acute intermittent porphyria
Miscellaneous: Guillian-Barre (acute infective polyneuritis)
Infections
Idiopathic
Drugs and chemicals
Deficiency states
Pheochromocytoma, Clinical characteristics: P^8
Palpitations
Pallor
Perspiration
Panic
Paroxysmal attacks
Pain: headache, chest, abdominal
Paradoxical rise in blood pressure with beta-blockers
Pregnancy-associated hypertension in some cases
Pneumonia, community-acquired, non-immunocompromised, causes: C PHLEMS
Chlamydia pneumoniae
Pneumococcus
Haemophilus influenzae
Legionella sp
Everything else
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Staphylococcus aureus
Post-menopausal Painless Vaginal Bleeding, causes: ACE
Atrophic vaginitis
Cervical carcinoma
Endometrial carcinoma
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, symptoms: IRAN
Insomnia and nightmares
Re-experiences of traumatic event at a later date
Arousal is increased
Numbing of general responsiveness to the real world
Potter Syndrome, features: POTTER
Pulmonary hypoplasia
Oligohydrominios
Twisted skin: wrinkly skin
Twisted face: Potter facies
Extremity defects
Renal agenesis: bilateral
Proptosis, causes: THE I
Tumour: retinoblastoma
Hemorrhage: traumatic posterior orbital hematoma
Endocrinopathy: Graves' disease
Infection: orbital cellulitis
Pupillary Dilation (persistent), causes: 3AM
3rd nerve palsy
Anti-muscarinic eye drops: to facilitate fundoscopy
Myotonic pupil (Holmes Adie pupil): most commonly in young women, with absent/delayed reaction to light and convergence, and of no pathological significance
Q
R
Rheumatic Fever, Jones' major diagnostic criteria: ACCES
Arthritis (ie: migratory arthritis)
Carditis
Chorea (ie: Sydenham's chorea or St Vidas' dance)
Erythema marginatum
Subcutaneous nodules
S
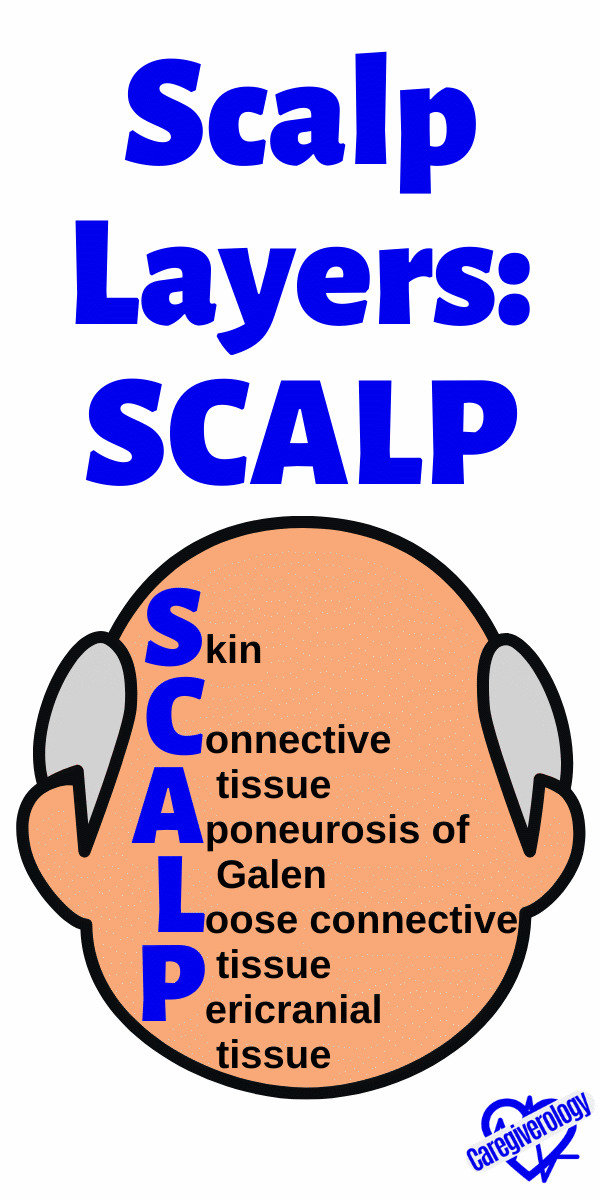
Scalp Layers: SCALP
Skin
Connective tissue
Aponeurosis of Galen
Loose connective tissue
Pericranial tissue
Scarlet Fever, signs and symptoms: SCARLET
Streptococcus pyogenes (ie: causative organism is group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus)
Circumoral pallor
Areas of desquamation of skin (late finding)
Rash (ie: sandpaper scarlatiniform rash, especially in axillae and groin)
Laryngitis/pharyngitis
Elevated temperature
Tongue (ie: initially, white strawberry tongue, then red)
Scoliosis, neuromuscular causes: M^4AC
Muscular dystrophy
Muscular atrophy: spinal muscle atrophy
Myelodysplasia
Mucocutaneous syndromes: neurofibromatosis
Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita
Cerebral palsy
Seizures in the Neonate, causes: H^5I
Hypoxia
Hypoglycemia
Hypocalcemia
Hypomagnesemia
Hemorrhage: periventricular, subarachnoid, subdural
Infection: fever, meningitis, TORCH organisms
Seriously Ill Pediatric Patient, recognition: SAVE A CHILD
Skin: mottled, cyanotic, petechiae, pallor
Activity: needs assistance, not ambulating, responsive
Ventilation: intercostal retractions, drooling, nasal flaring, respiratory rate, stridor, wheezing
Eye contact: glassy stare, fails to engage examiner
Abuse: unexplained bruising/injuries, inappropriate parent
Cry: high-pitched, cephalic, irritable
Heat: high fever > 41 C, hypothermia < 36 C
Immune system: AIDS, corticosteroids, asplenic, sickle cell
Level of consciousness: irritable, lethargic, convulsions, unresponsive
Dehydration: % of total weight lost with 1 mL = 1 g, capillary refill, fontanelle, mucous membranes, cold hands/feet, voiding, diarrhea, vomiting
SAVE: Observations made prior to touching the child
CHILD: History from caretaker and brief exam
Sexual Development in the Female, stages of: ABCDE
Accelerated growth: height
Breast development
Cunnus hair: vaginal
Distal hair growth: axillae
Endometrial sloughing: menarche
Shoulder Dislocation Posteriorally, causes: 3 E's
Epileptic seizure
Ethanol intoxication
Electrical injury: electrocution, electroconvulsive therapy
Splenomegaly, causes: CHICAGO
Cancer
Hem, onc
Infection
Congestion (portal hypertension)
Autoimmune (RA, SLE)
Glycogen storage disorders
Other (amyloidosis)
Splenomegaly, causes: CHINA
Congestion/cellular infiltration
Hematological (eg: hemolytic anemia, sickle cell)
Infection/infarction (eg: malaria, GF, CMV)
Neoplasia (eg: CML, lymphoma, other myeloproliferative)
Autoimmune
Splenomegaly, causes: IBM PCM
Infectious (eg: viral: Epstein-Barr, herpes; parasitic: malaria, schistosomiasis, babesiosis, kala-azar = visceral Leishmanniasis; bacterial: subacute bacterial endocarditis)
Blood disease (eg: hemolytic anemia, hereditary spherocytosis, hemoglobinopathies (ie: sickle-cell disease, thalassemias)
Malignancy (eg: Hodgkin's lymphoma, leukemias)
Portal hypertension (ie: Banti's syndrome)
Connective tissue disease (eg: sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, polyarteritis nodosa)
Miscellaneous (eg: Gaucher's disease, Niemann-Pick disease)
Stroke, etiology: LLACC
Lacunar: seen in basal ganglia and brain stem
Large-artery disease: Takayasu's arteritis, syphillis
Atherosclerotic: carotid artery-to-cerebral artery embolism
Cargiogenic: atheroma, bacterial vegetations in endocarditis
Coagulable (ie: hypercoagulable) states
Stroke, risk factors: HEADS
Hypertension/Hyperlipidemia
Elderly
Atrial fibrillation (a fib)
Diabetes mellitus/Drugs (cocaine)
Smoking/Sex (male)
Stroke, symptoms: FAST
If you act FAST, treatment is possible. Timing is key. The faster you act, the less likely disability or death will occur.
Face looks uneven: Ask them to smile. Does one side of the face droop?
Arm hanging down: Ask them to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
Speech slurred: Ask them to repeat a phrase. Does the speech sound odd?
Time is vital: If any of these signs are present, call emergency services right away.
Suicide, risk factors: SAD
Schizophrenia
Alcohol abuse
Depression
Suicide, risk scale: SAD PERSONS
Sex: male
Above 40 years of age
Depression
Previous suicide attempt
Ethanol abuse
Rational thinking lost
Support systems lost
Organized suicide plan
No spouse
Sickness: physical illness
If score 0-2: send home with family or friend
If 3-4: arrange cose follow-up or consider short admission
If 5-6: strongly consider hospitalization
If 7-10: hospitalize and watch closely
Synovial Fluid Analysis, 3 necessary tests: 3 C's
Cell count and differential
Crystal examination
Culture and gram stain
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), 11 diagnostic criteria: PRUNE RASH
Photosensitivity
Rashes: discoid, malar
Ulcers in mouth
Neurologic: seizures, psychosis
Elevated blood tests: raised antinuclear antibody, positive SLE cells seen, positive anti-double-stranded DNA antibody, positive anti-smooth muscle antibody, false-positive VDRL test
Renal: proteinuria, hematuria, cellular casts
Arthritis: non-erosive
Serositis: pleuritis, pericarditis, peritonitis
Hematologic: hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
Need 4 for diagnosis
T
Tachycardia, causes: MD PISH^3
Metabolic (eg: thyrotoxicosis)
Drugs (eg: sympathomimetics, anticholinergics)
Pain
Ischemia
Sepsis
Hypotension
Hypoxia
Hypercarbia
Thickened Nerves, causes: HANDS
Hansen's: leprosy
Amyloidosis
Neurofibromatosis
Diabetes mellitus
Sarcoidosis
Thyroid Malignancies, Age-associated types: PPMMAAF
Papillary carcinoma seen in Pediatric group
Medullary (parafollicular) carcinoma seen in Middle-aged group
Anaplastic carcinoma seen in Aged group
Follicular carcinoma seen in all groups
Trauma Patient, Initial assessment and management: ABC^4
Airway
Breathing
Circulation
Cervical spine injury
Chest: tension pneumothorax, flail chest, pericardial tamponade
Consciousness: assess level according to the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
Trauma Patient, Initial assessment and management: ABCDEF
Airway/breathing (C-spine stablilization is actually first)
Bleeding sites
Central nervous system
Digestive organs
Excretory organs (ie: urine color, quantity)
Fractures
Tricyclic Antidepressants, side effects: A^4
Anticholinergic: confusion, blurred vision, reduced lacrimation, reduced salivation, heart acceleration (tachycardia), urinary retention, constipation
Antihistaminic: sedation, weight gain
Anti-alpha 1 adrenergic: orthostatic hypotension
Arrhythmogenic: quinidine-like ventricular cardiac effects
Tuberculosis, antibiotics used: STRIPE
STreptomycin
Rifampicin
Isoniazid
Pyrizinamide
Ethambutol
Tuberculosis, treatment: PRIEST
Pyrazinamide
Rifampin
Isoniazid (INH)
Ethambutol
STreptomycin
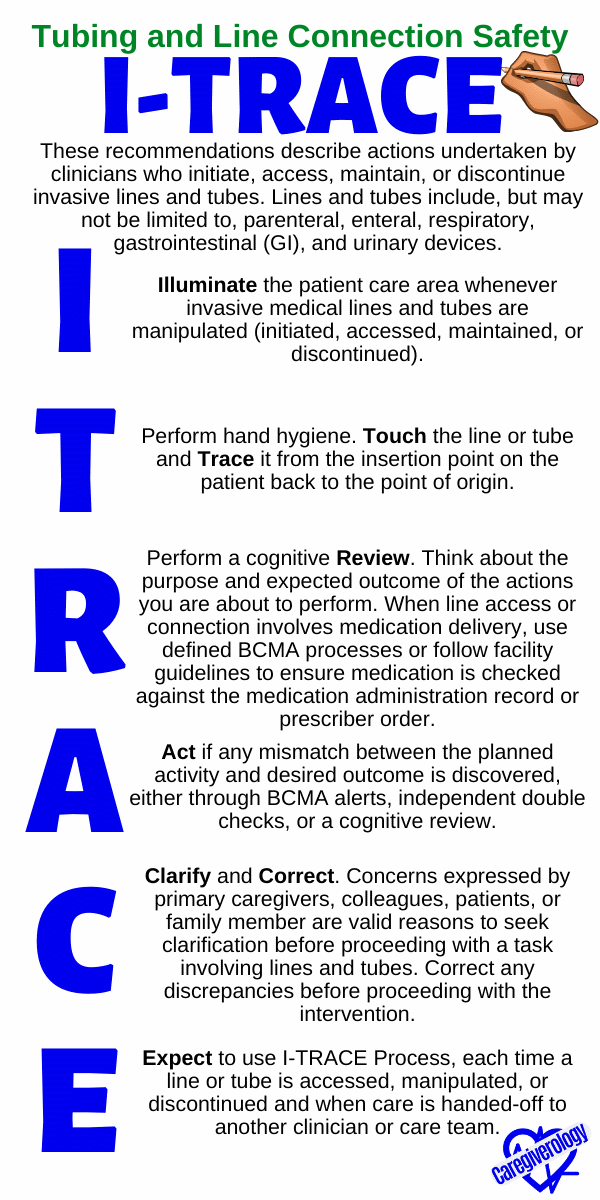
Tubing and Line Connection Safety: I-TRACE
Illuminate the patient care area whenever invasive medical lines and tubes are manipulated (initiated, accessed, maintained, or discontinued).
Perform hand hygiene. Touch the line or tube and Trace it from the insertion point on the patient back to the point of origin.
Perform a cognitive Review. Think about the purpose and expected outcome of the actions you are about to perform. When line access or connection involves medication delivery, use defined BCMA processes or follow facility guidelines to ensure medication is checked against the medication administration record or prescriber order.
Act if any mismatch between the planned activity and desired outcome is discovered, either through BCMA alerts, independent double checks, or a cognitive review.
Clarify and Correct. Concerns expressed by primary caregivers, colleagues, patients, or family member are valid reasons to seek clarification before proceeding with a task involving lines and tubes. Correct any discrepancies before proceeding with the intervention.
Expect to use I-TRACE Process, each time a line or tube is accessed, manipulated, or discontinued and when care is handed-off to another clinician or care team.
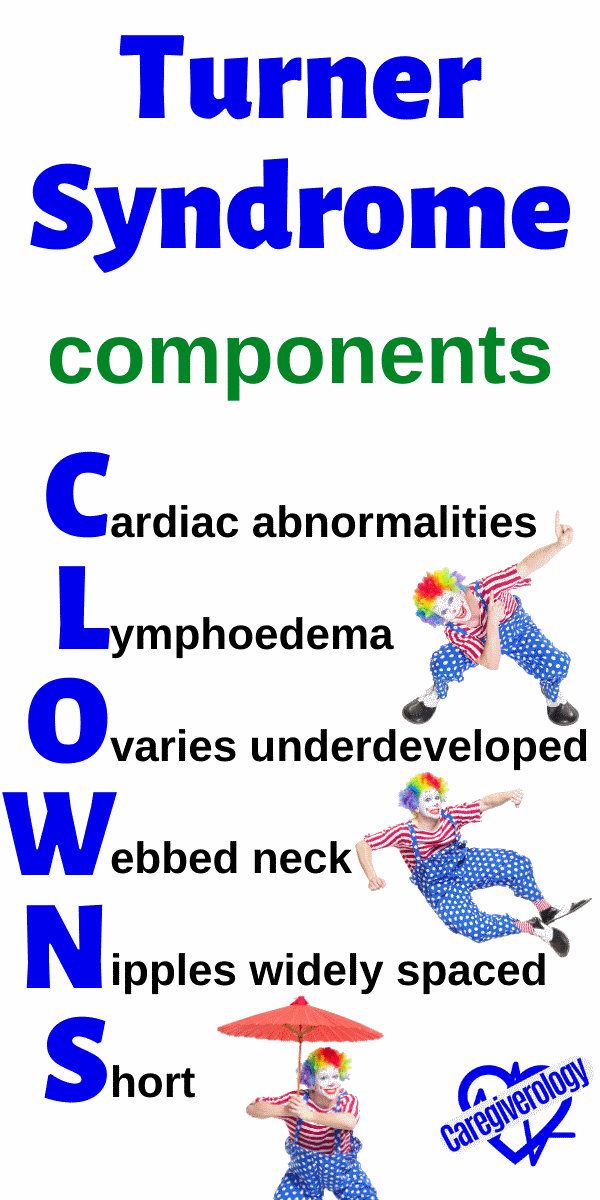
Turner Syndrome, components: CLOWNS
Cardiac abnormalities: coartication
Lymphoedema
Ovaries underdeveloped: sterility, amenorrhea
Webbed neck
Nipples widely spaced
Short
U
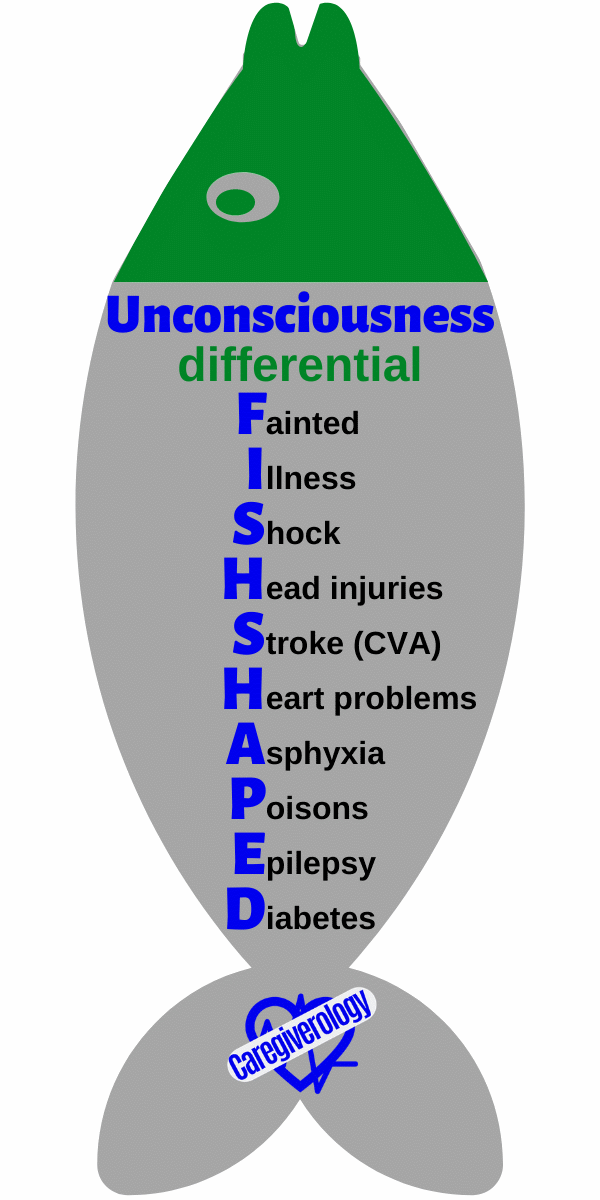
Unconsciousness, differential: FISH SHAPED
Fainted
Illness/Infantile febrile convulsions
Shock
Head injuries
Stroke (CVA)
Heart problems
Asphyxia
Poisons
Epilepsy
Diabetes
Unconscious Patient, initial considerations of causes: DEATHH
Diabetes mellitus: causing DKA, non-ketotic hyperosmolar coma, or hypoglycemia
Epilepsy
Alcohol or drugs
Trauma
Hypertension: causing hypertensive encephalopathy or stroke
Heart disease: causing myocardial infarction (MI)
Unconscious Patient, initial treatments when cause unknown: DONT Forget
Dextrose: 50 mL of 50% dextrose IV bolus
Oxygen: 40% by mask
Naloxone (narcan): 1 mg IV initially, to maximum 10 mg
Thiamine: 100 mg IV (give before dextrose)
Flumazenil: 0.1 mg IV push
Urinary Incontinence, causes of acute and reversible: DRIP
Delirium
Restricted mobility/Retention
Inflammation/Infection/Impaction: fecal
Pharmaceuticals/Polyuria
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI), common causative organisms: PEEKS
Proteus
E coli
Enterococcus
Klebsiella
Serratia
Uterine (Endometrial) Carcinoma, risk factors: HEAD
Hypertension
Estrogen Unopposed (ie: post-menopausal estrogen administration, nulliparity, late-onset menopause, polycystic ovary disease, obesity)
Atherosclerosis
Diabetes mellitus
V
Valve Disease, Causes: DIC
Degenerative (most common in North America)
Inflammatory (eg: lupus, rheumatic fever)
Congenital (eg: bicuspid aortic valve, Marfan's syndrome)
Venous Insufficiency, signs: STUBbED
Stasis dermatitis
Trendelenberg test positive
Ulceration of medial malleolus
Brown pigment coloration
b
Edema
Dependency pain (ie: painful when leg below body level)
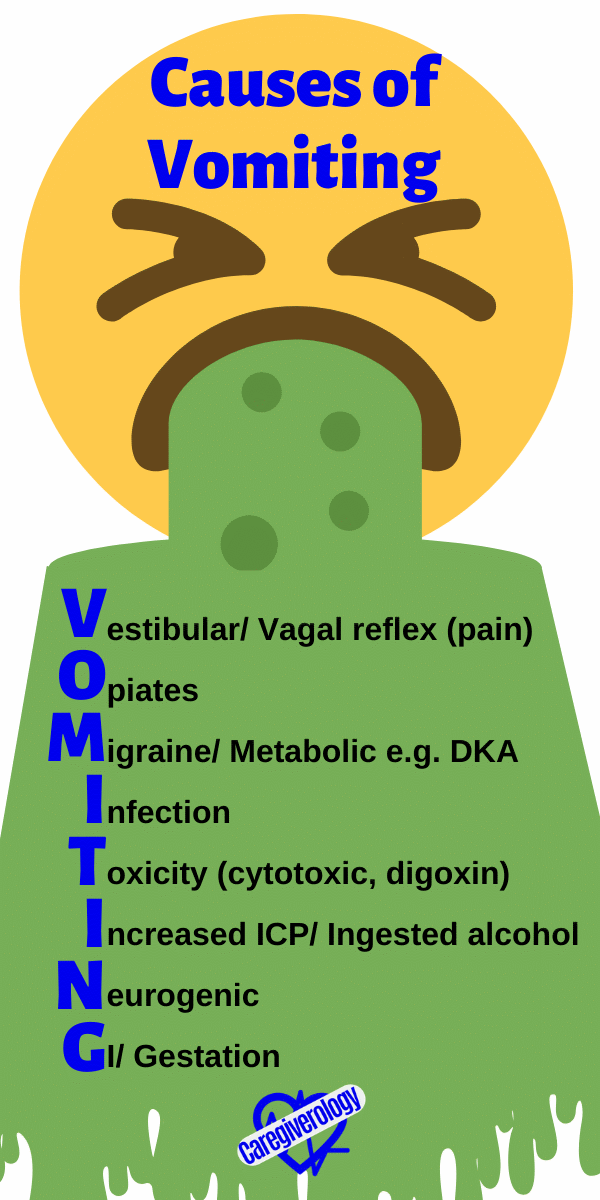
Vomiting, Causes of: VOMITING
Vestibular/ Vagal reflex (pain)
Opiates
Migraine/ Metabolic e.g. DKA
Infection
Toxicity (cytotoxic, digoxin)
Increased ICP/ Ingested alcohol
Neurogenic
GI/ Gestation
Vulvar Pruritus, differential diagnosis: ILL DOC
Infection: candidiasis, oxyuris vermicularis (pinworms), trichomonas vaginalis
Lichen sclerosis et atrophicus
Lichen simplex (ie: neurodermatitis)
Diabetes mellitus
Oestrogen deficiency (ie: post-menopausal)
Contact dermatitis
W
Wernicke-Korsakoff's Psychosis, findings: COAT RACK
Wernicke's encephalopathy (acute phase):
Confusion
Ophthalmoplegia
Ataxia
Thiamine tx
Korsakoff's psychosis (chronic phase):
Retrograde amnesia
Anterograde amnesia
Confabulation
Korsakoff's psychosis
X
Y
Z
Pin this content!
Medical References for Caregivers
From Many Medical Mnemonics for Memorization to Home
Reference:
http://www.stmichaelshospital.com/pdf/research/mapped-medical-mnemonics.pdf
Recent Articles
-
What to Expect During Post-Operative Recovery at Home - Caregiverology
Apr 08, 25 08:21 PM
Surgery may be over, but the journey to full recovery is just beginning, and for many people, the hardest part happens after they leave the hospital. -
How to Plan for Aging: Financial, Health, and Lifestyle Considerations
Mar 29, 25 12:40 PM
Did you know that 70% of people over 65 will need some form of long-term care? Yet, many delay planning until it’s too late. Aging is inevitable, but how we experience it depends on preparation. -
Speech Disorders: How to Know When It's Time to See a Professional
Mar 27, 25 07:05 AM
When it comes to human interaction, we need to be able to communicate effectively.


























New! Comments
Have something to say about what you just read? Leave a comment in the box below.